JAMAICAN CHRISTMAS


https://www.google.com/maps/place/Kingston,+Jamaica

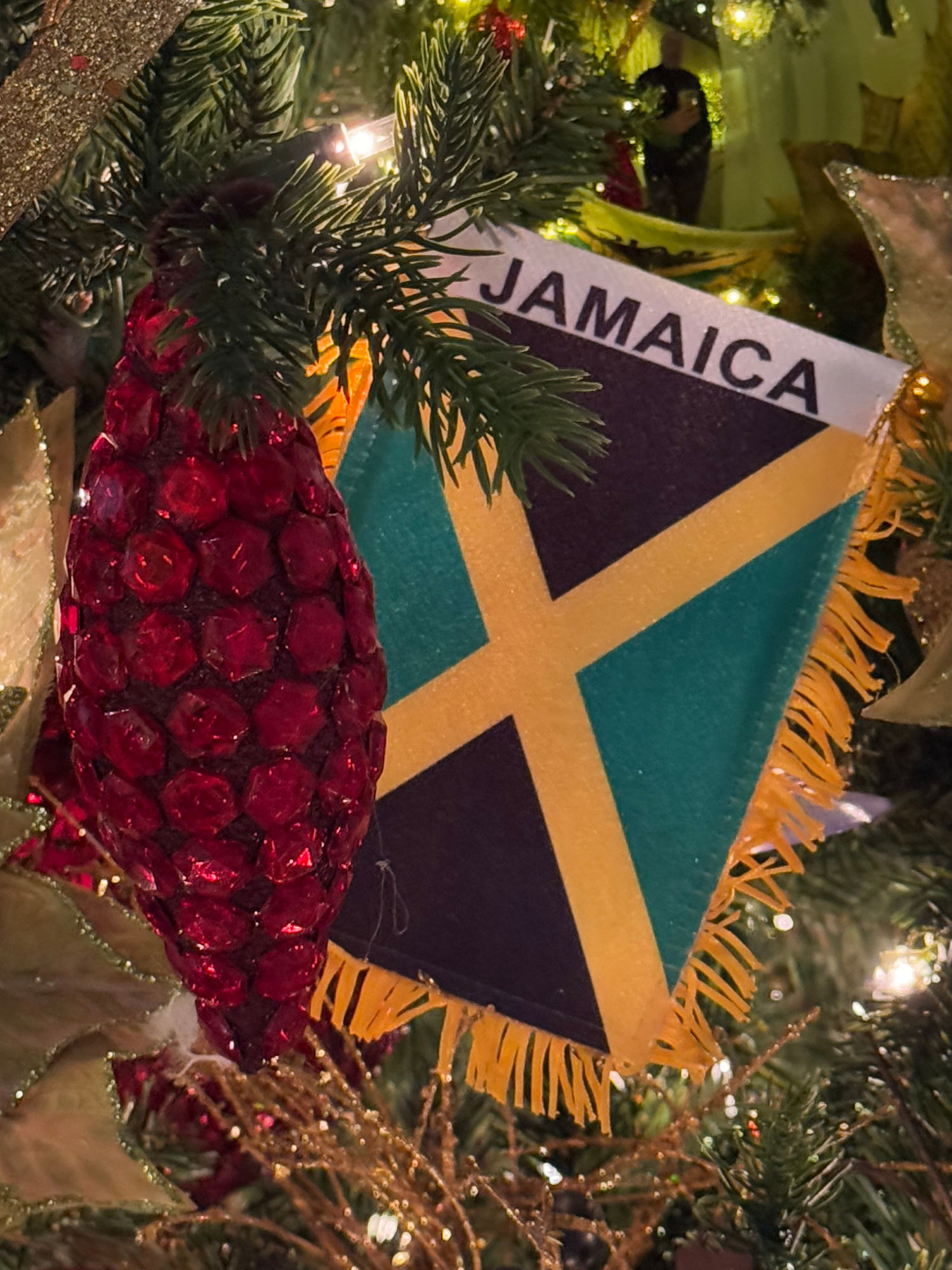
Christmas is a very special time in Jamaica and like a lot of other countries, radio stations play carols all through the Christmas period.Lots of people paint their houses and hang new curtains and decorations for Christmas. Most families spend Christmas Day at home with friends and family members.
In Jamaica, on Christmas Eve the 'Grand Market' happens. It is a really exciting time, especially for children. In every town and city there is a cross between a festival and a market. During the day, people go shopping for Christmas foods, sweets and toys, etc. You might also buy some new clothes ready for the celebrations in the evening. (But you don't want to spend all your money during the day as there were lots of great things to buy in the evening as well!)
Around 6.00pm the evening part of Grand Market starts and it lasts until the morning! Everyone comes out on their new or best clothes, including children, to celebrate and party all night. All the streets, shops and many houses are decorated with lights. There are normally street vendors selling food like jerk chicken, boiled corn, and sweets like candy canes and sugarcane.
Following the Grand Market, some people will go to a Midnight Mass Church Service and others will party all night. Many people will also go to a Church Service on Christmas Day morning before the end of Grand Market.
The Christmas day meal is usually prepared on Christmas Eve. The Christmas Day breakfast includes ackee and saltfish, breadfruit, fried plantains, boiled bananas, freshly squeezed fruit juice and tea. Dinner is usually served in the late afternoon and this may include turkey, chicken, curry goat, stewed oxtail and very importantly rice and peas.
Jamaican red wine and rum fruitcake is traditional and is eaten in most homes. The fruits in the cake are soaked in red wine and white rum for months before Christmas. (I have some friends who come from Jamaica and Jamaican Christmas Cake is really nice!)
In Jamaican Creole / Patois it's Merri Crissmuss

CULTURE TRIPChristmas In Jamaica
Jamaica has more churches per square mile than any other country in the world, so it's not surprising that Christmas is one of the most important religious and cultural celebrations. Festivities run from early December to New Year's Day, with non-stop parties and family gatherings. Despite the distinct lack of snow and chimneys, Santa Claus still visits Jamaica and gift giving is part of the tradition. Here's how to celebrate a tropical Christmas Jamaican style.Christmas Preparations
The temperature drops slightly as the crismus breeze arrives in early December, making things more comfortable and marking the start of the season. Towns and cities create a festive atmosphere by decorating the streets and palm trees with brightly colored Christmas lights known locally as pepper lights. Houses in affluent neighborhoods compete to create the best light displays, and even local taxis are decorated.Christmas trees are everywhere; the plastic kind may dominate, but locally grown Blue Mountain pines are more elegant. Grown high up in the lush mountains, they are a softer, lighter alternative to the Norwegian pine. It is also traditional to decorate the home with bright red Poinsettias at Christmas. They're so popular that it can be necessary to pre-order them months in advance.
Christmas Eve
The long standing tradition of Gran Market is one of the biggest days of the year for many Jamaicans – especially children. From Christmas Eve until Christmas morning, vendors gather to sell their wares at key locations around the country. Festivities continue through the night into the early hours of Christmas morning, keeping shoppers entertained. The best Gran Market in Jamaica is found in Linstead, St Catherine. It is a shoppers' paradise, offering the opportunity to buy everything from last-minute gifts and Christmas decorations to clothing and food. However, many people attend just to enjoy the party atmosphere.The traditional masquerade party of 'John Canoe' or Jonkanoo is one of the highlights of 'Gran Market'. It involves people dressing up and wearing masks while dancing though the streets to accompanying music. The Jonkanoo tradition came to Jamaica with slaves from Africa and was once popular across the island. Now it is more confined to the rural areas.
Christmas Day
Christmas Day starts with a traditional Jamaican breakfast of ackee & saltfish, breadfruit and boiled bananas. Families will normally then attend church. Mass is an important aspect of Christmas for most Jamaicans, who turn out in their 'Sunday best' for this special day. Christmas mass is a joyous celebration with enthusiastic carol singing and hand clapping. Steel drums and reggae versions of popular Christmas songs give an unmistakably Caribbean feel to the day.Christmas dinner is a big event that brings family and friends together to celebrate and feast. Roast turkey is notably absent from most Jamaican dinner tables and replaced with curried goat, roast chicken and a much-loved ham. Rice and peas take on a Christmas twist, being made with pigeon peas instead of red kidney beans. The food is accompanied by that seasonal favourite drink Sorrel – usually made with a generous portion of rum. The traditional dessert of rum-laden fruit cake finishes the meal.
Boxing Day
The party starts again in Kingston on Boxing Day with the National Pantomime performance of The Upsies and de Downzies dem . The Little Theatre Movement, a Jamaican institution, held its inaugural panto on December 26th, 1941 and has done so annually ever since. This Christmas show is a celebration of Jamaican culture, folklore and history.The famous dancehall show, Sting (no relation to Sting of Police fame), also takes place on Boxing Day evening. For dancehall fans everywhere, this is unmissable. The show usually starts at 8pm but the real entertainment rarely begins before midnight. In short, December is non-stop party season with all kinds of celebrations taking place, from beach parties to huge public sound system events and everything in between.


WORLD HOLIDAY TRADITIONSHoliday Traditions of Jamaica
Despite the lack of snow and chimneys in Jamaica, Santa Claus still visits children, and gift giving is part of the Christmas traditions. Radio stations start playing Christmas carols early, some as early as October. As Jamaica is the home of reggae music, they play reggae remixes.Decorating also starts up early. Houses are painted festive colors, Christmas lights, called "pepper lights", are strewn about neighborhoods, towns, and trees, and elaborate ornaments, curtains, table cloths, and place settings deck the homes. Locally grown Blue Mountain pines make a good alternative to the typical Norwegian pines found in more northern climates. Poinsettias are so popular in the decorating that they need to be pre-ordered months in advance.
Christmas concerts, parties, and balls are very popular leading up to Christmas Day and can be found virtually anywhere; community centers, city squares, and even at churches. Many of these will last until the break of day.
The biggest of all these festivities by far is the Grand Market. From Christmas Eve until Christmas morning, vendors gather together in every town to sell last-minute gifts, toys, decorations, clothing, and lots of food in a party atmosphere. The real fun begins at sunset; the music, dancing, and partying goes on all night, keeping the shoppers well entertained. The best Grand Market is found in Linstead, St. Catherine.
Another tradition, John Canoe, or Jonkanoo, a masquerade procession, came to Jamaica from their African ancestors. Once a popular tradition across the island, it's more confined to rural areas nowadays.
Jamaica has more churches per square mile than any other country in the world, and as such Christmas is one of the island's most important celebrations. Following the Grand Market, many people will attend a midnight mass service. Others will continue parting all night, and attend a Christmas Day morning service instead. Church goers put on their Sunday best and celebrate with carol singing, hand clapping, and reggae versions of Christmas songs.
The traditional Christmas Day breakfast includes ackee, saltfish, breadfruit, fried plantains, boiled bananas, and some freshly squeezed fruit juice or tea to wash it all down with. Dinner is typically served in the late afternoon. The main courses are curried goat, pork, chicken, and oxtail, all served with rice and gungo peas. The more affluent families include ham and imported turkey. For dessert, there's the seasonal favorite drink sorrel and the Jamaican Christmas Cake, for which fruits are soaked in red wine and white run for months before Christmas.
On Boxing Day, December 26th, the National Pantomime performance of The Upsies and de Downzies Dem by the Little Theatre Movement has been an annual celebration of Jamaican culture, folklore, and history since 1941. And in the evening, be sure to catch the famous dancehall show Sting.

JAMAICANStay Irie: - Everything is alright
CULTURE TRIPJamaican Christmas Dishes
Christmas is one of the most important festivals on the Jamaican calendar. This is a time for family reunions and spending time with loved ones, and the foods Jamaicans eat at Christmas are a big part of this important celebration. There are many traditions and conventions to be respected when planning Christmas meals in Jamaica and expectations are high.Sorrel
Most visitors to a Jamaican home at Christmas will expect a glass or two of Jamaican sorrel, often accompanied by a slice of Christmas cake. This delicious crimson colored Christmas drink, made from the sepals of the sorrel flower, is Jamaica's own version of mulled wine. The plant is essentially stewed with ginger and spices, then sieved when cooled. White rum is often added at the end.Christmas Cake or Christmas Pudding
To Jamaicans, the terms Christmas cake and Christmas pudding mean the same thing; a deliciously rich fruit cake. Packed with rum, it is a staple in most Jamaican homes throughout the festive season. The cake is packed with fruits that have been soaked in wine or rum, usually for weeks or months in advance. It is customary to offer a piece to visitors who drop by during the holidays, and to eat a big slice on Christmas Day.Curried Goat
Curried goat is a staple for most Jamaican households on Christmas Day. Often curried on the bone, this spicy goat dish is usually served with rice and gungo peas. Nothing of the goat is wasted; the animal's entrails will make a hearty soup called mannish water that is noted for its aphrodisiac properties.Egg Punch
The traditional drink of egg punch is usually prepared by Jamaican mothers before church on Christmas Day. This Jamaican version of eggnog is so popular it can be purchased from supermarkets in cartons. One local variation includes the addition of Guinness Stout, lending a fortifying quality to this Christmas tradition.Gungo Peas
Also known as pigeon peas, these come into season just in time for Christmas. They are used in the Christmas variation of that Jamaican staple rice and peas, the gungo peas replacing the usual red beans. Another popular dish is gungo pea soup, made with the bone of the Christmas ham. The soup is often served with dumplings as a Christmas treat.Christmas Ham
For many Jamaicans, Christmas is not complete without a leg of roasted ham. Heavily seasoned and marinated, it goes into the oven early on Christmas morning and makes its grand entrance to the table dressed in an assortment of cherry and pineapple decorations. This is an expensive luxury in Jamaica that not every family will serve. The ham is usually the most popular item on the buffet table at Christmas parties.



President Reagan Nancy Reagan Edward Seaga Mrs. Seaga are greeted by children at an arrival ceremony at the Norman Manley Airport in Kingston Jamaica.
Reagan's Daily DiaryWednesday, April 7, 1982
8:10 A.M. meeting on the So. Atlantic problem then off to Barbados-well Jamaica 1st at 10 A.M.Key Facts
- President Reagan begins a five-day "working holiday" in the Caribbean.
- Iran's minister of Foreign affairs Ghotbzadeh is arrested and later executed.
RONALD REAGANRemarks on Arrival in Kingston, JamaicaApril 7, 1982
Well, Prime Minister Seaga and Mrs. Seaga, Nancy and I are very glad to see you again and appreciate very much meeting the distinguished members of your government who are here today.
When we met in Washington just after I took office, you told me of the energy, the skills, and the creative genius of your people. You told me of the beauty of this country and the hospitality of its people. Well, Nancy and I are delighted to have your kind invitation to visit Jamaica as so many Americans do each year.
When we last met, we agreed on the importance of the Caribbean and the need to take vigorous action to strengthen the democratic governments and economies of Jamaica and our neighbors. Our talks convinced me that the talents of the Jamaican people, the peoples throughout the Caribbean, are the hope for the economic recovery of this region so near and so vital to all of us. The progress that you are making here with your own program shows what can be done when people living in a democratic society are given the opportunity to work and to enjoy the fruits of their labor.
As we agreed in Washington, the United States can best help by expanding the opportunity of your people and those of your neighbors to trade freely with us, to give them a chance to produce and sell their products in a competitive, free market. Trade lies at the heart of the proposals I sent to the Congress on March 17th to begin the initiative that we've been planning for almost a year. Our discussions here in Kingston will be valuable to me in learning how we can best go forward in carrying out the plans that we've laid. I learned a great deal from our earlier discussions, and I know these will be equally useful.
The success of our venture depends on cooperation, and cooperation is easier between friends who share the same ideals. For this reason we're pleased to find ourselves working together with the leaders of countries with such strong democratic traditions.
Jamaica is known in the United States not only for its beauty but for the courage of its people and the freedom they cherish and staunchly defend. Jamaica is an inspiration to all of us who believe economic development and freedom are compatible and in practice are mutually reinforcing. Freedom enhances the creativity of man. The reality of economic progress strengthens the people's faith in freedom.
I'm looking forward to our meetings with you and your Ministers and discussing the entire range of issues in our relationship. I know they will strengthen the already close ties of friendship between our two countries and continue the progress toward the goals of freedom and prosperity we seek for the Caribbean.
Thank you.
NOTEThe President spoke at 2:10 p.m. at the Norman Manley International Airport, where he was greeted by Loren E. Lawrence, U.S. Ambassador to Jamaica, Prime Minister and Mrs. Edward Philip George Seaga, and a delegation of Jamaican officials.Following their arrival, the President and Mrs. Reagan paid a courtesy call on the Governor General of Jamaica, Sir Florizel Glasspole, and Lady Glasspole, at King's House, the Governor General's residence.
WIKIPEDIAJamaica
An island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning 10,990 square kilometres (4,240 sq mi) in area, it is the third largest island - after Cuba and Hispaniola - of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about 90 miles south of Cuba, and 119 miles west of Hispaniola (the island containing the countries of Haiti and the Dominican Republic); the British Overseas Territory of the Cayman Islands lies 134 miles to the north-west.Originally inhabited by the indigenous Taino peoples, the island came under Spanish rule following the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1494. Many of the indigenous people either were killed or died of diseases, after which the Spanish brought large numbers of African slaves to Jamaica as labourers. The island remained a possession of Spain until 1655, under the name Santiago, when England (later Great Britain) conquered it and named it Jamaica. It became an important part of the colonial British West Indies.
Under Britain's colonial rule, Jamaica became a leading sugar exporter, with a plantation economy dependent on continued importation of African slaves and their descendants. The British fully emancipated all slaves in 1838, and many freedmen chose to have subsistence farms rather than to work on plantations. Beginning in the 1840s, the British began using Chinese and Indian indentured labor to work on plantations. The island achieved independence from the United Kingdom on 6 August 1962.
- With 2.8 million people, Jamaica is the third-most populous Anglophone country in the Americas (after the United States and Canada), and the fourth-most populous country in the Caribbean.
- Kingston is the country's capital and largest city.
- The majority of Jamaicans are of Sub-Saharan African ancestry, with significant European, East Asian (primarily Chinese), Indian, Lebanese, and mixed-race minorities.
- Due to a high rate of emigration for work since the 1960s, there is a large Jamaican diaspora, particularly in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- The country has a global influence that belies its small size; it was the birthplace of the Rastafari religion, reggae music (and associated genres such as dub, ska and dancehall), and it is internationally prominent in sports, most notably cricket, sprinting and athletics.
- Jamaica has sometimes been considered the world's least populous cultural superpower.
- Jamaica is an upper-middle income country with an economy heavily dependent on tourism; it has an average of 4.3 million tourists a year.
- The country performs favorably in measures of press freedom, democratic governance and sustainable well-being.
- Jamaica is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy with power vested in the bicameral Parliament of Jamaica, consisting of an appointed Senate and a directly elected House of Representatives. Andrew Holness has served as Prime Minister of Jamaica since March 2016. As a Commonwealth realm, with Charles III as its king, the appointed representative of the Crown is the Governor-General of Jamaica, an office held by Patrick Allen since 2009.
- Jamaica is the third largest island in the Caribbean.
- The climate in Jamaica is tropical, with hot and humid weather, although higher inland regions are more temperate.
- Jamaica lies in the hurricane belt of the Atlantic Ocean and because of this, the island sometimes suffers significant storm damage.
- Jamaica's diverse ethnic roots are reflected in the national motto "Out of Many One People". Most of the population of 2,812,000 (July 2018 est.) are of African or partially African descent, with many being able to trace their origins to the West African countries of Ghana and Nigeria.
- Jamaica is regarded as a bilingual country, with two major languages in use by the population. The official language is English, which is "used in all domains of public life", including the government, the legal system, the media, and education. However, the primary spoken language is an English-based creole called Jamaican Patois (or Patwa).
- When Jamaica gained independence in 1962, the murder rate was 3.9 per 100,000 inhabitants, one of the lowest in the world. By 2009, the rate was 62 per 100,000 inhabitants, one of the highest in the world.
- Christianity is the largest religion practiced in Jamaica.
- Jamaican culture has a strong global presence. The musical genres reggae, ska, mento, rocksteady, dub, and, more recently, dancehall and ragga all originated in the island's vibrant, popular urban recording industry. Some rappers, such as The Notorious B.I.G., Busta Rhymes, and Heavy D, are of Jamaican descent. Bob Marley is probably the best known Jamaican musician; with his band the Wailers he had a string of hits in 1960s–70s, popularizing reggae internationally and going on to sell millions of records.
- The island is famous for its Jamaican jerk spice, curries and rice and peas which is integral to Jamaican cuisine. Jamaica is also home to Red Stripe beer and Jamaican Blue Mountain Coffee.
- While the most popular local sport is cricket, on the international stage Jamaicans have tended to do particularly well at track and field athletics. Over the past six decades Jamaica has produced dozens of world class sprinters including Olympic and World Champion Usain Bolt. Association football and horse-racing are other popular sports in Jamaica. The Jamaica national bobsled team was once a serious contender in the Winter Olympics, beating many well-established teams. Chess and basketball are also widely played in Jamaica.
- Jamaica's agricultural exports are sugar, bananas, cocoa, coconut, molasses oranges, limes, grapefruit, rum, yams, allspice (of which it is the world's largest and "most exceptional quality" exporter), and Blue Mountain Coffee which is considered a world renowned gourmet brand.
EtymologyThe indigenous people, the Taino, called the island Xaymaca in their language, meaning the "Land of Wood and Water" or the "Land of Springs". Yamaye has been suggested as an early Taino name for the island as recorded by Christopher Columbus. Colloquially, Jamaicans refer to their home island as the "Rock". Slang names such as "Jamrock", "Jamdown" ("Jamdung" in Jamaican Patois), or briefly "Ja", have derived from this.














