RUSSIAN CHRISTMAS


https://www.google.com/maps/place/Moscow,+Russia

| HOW TO SAY MERRY CHRISTMAS: | |
|---|---|
| In Russian | S Rozhdestvom |


WHYCHRISTMAS.COMChristmas in Russia
In the days of the Soviet Union, Christmas was not celebrated very much. New Year was made into the important time. Following the revolution in 1917, Christmas was banned as a religious holiday in 1929 and Christmas Trees were banned until 1935 when they turned into 'New Year' Trees! If people did want to celebrate Christmas, they had to do it in secret just in their families.After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, people were free to celebrate Christmas again. But it's still a quieter and smaller holiday in Russia after the big New Year celebrations.
The New Year is the big time for spending lots of money and eating and drinking lots. Christmas is much more religious and private.
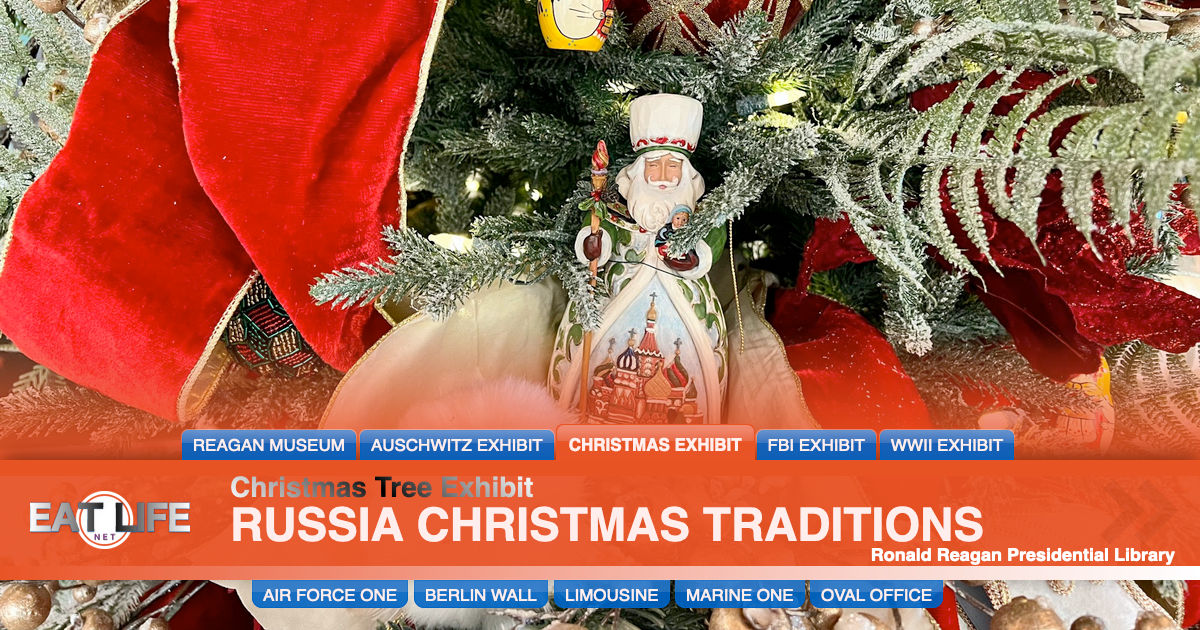
New Year is also when 'Grandfather Frost' (known in Russian as Ded Moroz) brings presents to children. He is always accompanied by his Granddaughter (Snegurochka). On New Year's eve children hold hands, make a circle around the Christmas tree and call for Snegurochka or Ded Moroz. When they appear the star and other lights on the Christmas tree light up! Ded Moroz carries a big magic staff. The traditional greeting for Happy New Year is S Novym Godom.
On New Year's Eve, a popular and now 'traditional' film to watch on TV is called 'The Irony of Fate' (or Ironiya sudby). It's also known as 'Enjoy your Bath' or 'With a Light Steam' and was made in 1975 during the Soviet era and was always shown on Soviet TV on New Year's Eve. It's a romantic comedy about a man who drinks too much and gets very lost after having a sauna with some of his friends. The Irony of Fate is also shown on Russian TV on New Year's Eve. It's also shown on New Year's Eve in Belarus.
Christmas in Russia is normally celebrated on January 7th (only a few Catholics might celebrate it on the 25th December). The date is different because the Russian Orthodox Church uses the old 'Julian' calendar for religious celebration days. The Orthodox Church also celebrates Advent. But it has fixed dates, starting on 28th November and going to the 6th January, so it's 40 days long.
The official Christmas and New holidays in Russia last from December 31st to January 10th.
In Russian Merry Christmas is s-rah-zh-dee-st-VOHM or s-schah-st-lee-vah-vah rah-zh dee-st-vah
- Some people fast (don't eat certain foods) on Christmas Eve, until the first star has appeared in the sky. People then eat 'sochivo' or 'kutia' a porridge made from wheat or rice served with honey, poppy seeds, fruit (especially berries and dried fruit like raisins), chopped walnuts or sometimes even fruit jellies!
- Kutia is sometimes eaten from one common bowl, this symbolizes unity. In the past, some families like to throw a spoonful of sochivo up on the ceiling. If it stuck to the ceiling, some people thought it meant they would have good luck and would have a good harvest!
- The Russian word for Christmas Eve 'sochelnik', comes from the word 'sochivo'.
- Some Orthodox Christian Russians also don't eat any meat or fish during the Christmas Eve meal/feast.
- Other popular Christmas Eve foods include, beetroot soup (borsch) or vegan potluck (solyanka) served with individual vegetable pies (often made with cabbage, potato, or mushroom); sauerkraut, porridge dishes such as buckwheat with fried onions and fried mushrooms, salads often made from vegetables like gherkins, mushrooms or tomatoes, and also potato or other root vegetable salads. The meal often consists of 12 dishes, representing the 12 disciples of Jesus.
- 'Vzvar' (meaning 'boil-up') is often served at the end of the meal. It's a sweet drink made from dried fruit and honey boiled in water. Vzvar is traditionally at the birth of a child, so at Christmas it symbolizes the birth of the baby Jesus.
- Following the meal, prayers might be said and people then go to the midnight Church services. They often don't wash the dishes until they get home from Church - sometimes not until 4.00am or 5.00am!
- The main meal on Christmas day is often more of a feast with dishes like roast pork & goose, Pirog and Pelmeni (meat dumplings). Dessert is often things like fruit pies, gingerbread and honeybread cookies (called Pryaniki) and fresh and dried fruit and more nuts.
- There are Russian Christmas cookies called Kozulya which are made in the shape of a sheep, goat or deer.
- In some areas, children will go carol singing round the homes of friends and family and to wish people a happy new year. They are normally rewarded with cookies, sweets and money.



WHYCHRISTMAS.COMThe Story of Babushka
To people in western Europe and the USA, one of the most famous things about Christmas in Russia is the story of Babushka. Babushka means Grand Mother in Russian. It tells the story of an old women who met the Wise men on their way to see Jesus.However, most people in Russia have NEVER heard of the story as it was probably created by an American poet and writer called Edith Matilda Thomas in 1907! I've had many emails from Russian visitors to the site who have never heard the story before!
The Story of Babushka
Once in a small Russian town, there lived a women called Babushka. Babushka always had work to do sweeping, polishing, dusting and cleaning. Her house was the best kept, most tidy house in the whole village. Her garden was beautiful and her cooking was wonderful. One evening she was busy dusting and cleaning, so busy that she didn't hear all the villagers outside in the village square talking about and looking at the new star in sky.She had heard about the new star but thought, "All this fuss about a star! I don't even have the time to look because I'm so behind with my work. I must work all night!" So, she missed the star as it shone brightly, high overhead. She also missed the little line of twinkling lights coming down towards the village at dawn. She didn't hear the sounds of the pipes and drums. She missed the voices and whispers of the villagers wondering whether the lights were an army or a procession of some sort. She missed the sudden quiet of the villagers and even the footsteps coming up the path to her door. But the one thing that she couldn't miss was the loud knocking on her front door!
"Now what is that?" she wondered, opening the door. Babushka gaped in amazement. There were three kings at her door with one of their servants! "My masters need a place to rest," the servant said, "and yours is the best house in the village." "You want to stay here?" asked Babushka. "Yes, it would only be until night falls and the star appears again." the servant replied. Babushka gulped. "Come in, then." she said.
The kings were very pleased when they saw all of the of the home-baked bread, pies and cakes. She dashed about, serving them, asking lots of questions. "Have you come a long way?" "A very long way." sighed Caspar. "Where are you going?" "We're following the new star." said Melchior. "But where?" The kings didn't know, but they believed that it would lead the to a new-born king, a King of Earth and Heaven. "Why don't you come with us?" asked Balthasar. "You could bring him a gift like we do. I bring gold, and my colleagues bring spices and perfumes." "Oh, I'm not sure that he would welcome me," said Babushka, "and what could I bring for a gift? Toys! I know I could bring a toy. I've got a cupboard full of toys." she said sadly. "My baby son, died when he was small." Balthasar stopped her as she went to tidy the kitchen up. "This new king could be your king too. Come with us when the star appears tonight." he said. "I'll think about it." sighed Babushka.
As the kings slept, Babushka tidied up as quietly as she could. "What a lot of extra work there was!" she thought, "and this new king, what a funny idea, to go off with the kings to find him."
Babushka shook herself. There was no time for dreaming, all this washing-up and putting away had to be done. "Anyway," she thought, "how long would she be away? What would she wear? What about the gift?" She sighed. "There is so much to do. The house will have to be cleaned when they've gone. I couldn't just leave it." Suddenly it was night-time again and the star was in the sky. "Are you ready, Babushka?" asked Balthasar. "I'll come tomorrow," Babushka called, "I must just tidy here first and find a gift."
The kings went away sadly. Babushka ran back into her house, keen to get on with her work.
Finally, she went to the small cupboard, opened the door and gazed at all the toys. But they were very dusty. They weren't fit for a baby king. They would all need to be cleaned. She cleaned all of the toys until each one shined. Babushka looked through the window. It was morning! The star had came and gone. The kings would have found somewhere else to rest by now. She could easily catch them up, but she felt so tired. She had to sleep. The next thing she knew, she was awake and it was dark outside. She had slept all day! She quickly pulled on her cloak, packed the toys in a basket and ran down the path the kings had taken.
Everywhere she asked "Have you seen the kings?" "Oh yes," everyone told her, "we saw them. They went that way." For a day Babushka followed the trail of the kings and the villages got bigger and became towns. But Babushka never stopped. Then she came to a city. "The palace," she thought. "That's where the royal baby would be born." "No, there is no royal baby here," said the palace guard when she asked him. "What about three kings?" asked Babushka. "Oh yes, they came here, but they didn't stay long. They were soon on their journey." "But where to?" asked Babushka. "Bethlehem, that was the place. I can't imagine why. It's a very poor place. But that's where they went." replied the guard. She set off towards Bethlehem. It was evening when Babushka arrived at Bethlehem and she had been traveling for a long time. She went into the local inn and asked about the kings. "Oh yes," said the landlord, "the kings were here two days ago. They were very excited, but they didn't even stay the night." "And what about a baby?" Babushka cried. "Yes there was." Said the landlord. "The kings asked about a baby, too." When he saw the disappointment in Babushka's eyes, he stopped. "If you'd like to see where the baby was," he said quickly, "it was across the yard there. I couldn't offer the couple anything better at the time. My inn was really full, so they had to go in the stable."
Babushka followed him across the yard. "Here's the stable." he said. He left her in the stable. "Babushka?" Someone was calling her from the doorway. He looked kindly at her. She wondered if he knew where the family had gone. She knew now that the baby king was the most important thing in the world to her. "They have gone to Egypt, and safety," he told Babushka. "And the kings have returned to their countries. But one of them told me about you. I am sorry but you are too late. It was Jesus that they found, the world's Savior."
Babushka was very sad that she had missed Jesus and it is said that Babushka is still looking for him.

WORLD HOLIDAY TRADITIONSHoliday Traditions of Russia
In Russia, Christmas is celebrated on January 7th because the Russian Orthodox Church uses the Julian calendar for religious celebrations. Because of this, it's not uncommon for Russians to observe two Christmases and two New Year's Days-with the first Christmas on December 25th, and the second New Year's on January 14th. Orthodox Christians also celebrate Advent, the forty day period before Christmas which commemorates the arrival of Jesus into the world (Advent comes from the latin "Adventus", or arrival). Some will celebrate Advent by adhering to a strict vegan "fast", while others will abstain from eating altogether.The official Christmas/New Year holiday season in Russia lasts from December 31st to January 10th. Christmas was banned as a religious holiday under the reign of the Soviet Union in 1929, and as a result New Year's Day was made into the bigger celebration; if people wanted to celebrate Christmas, they had to do so in secret. After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, people were free to celebrate Christmas again, but to this day it still remains the smaller, quieter holiday following the big New Year's celebrations.
The Russian Santa Claus is Father Frost, known as Ded Moroz in Russian, who brings presents to children, accompanied by his Granddaughter Snegurochka, the snow maiden. Father Frost carries a staff, wears valenki, or felt boots, and rides across Russia in a troika, a vehicle led by three horses.
On Christmas Eve, some people fast until they see the first star in the sky. Then they break their fast with a meatless dinner. One traditional Russian Christmas Eve dish is sochivo or kutya, a porridge made from wheat or rice, served with honey, poppy seeds, fruit, and chopped walnuts. This dish is sometimes eaten from one common bowl to symbolize unity. The Russian word for Christmas Eve "sochelnik" comes from the word "sochivo". Other popular foods for this meal include beetroot soup or borsch, solyanka, a salty stew, served with individual vegetable pies made with cabbage, potato, or mushroom, sauerkraut, porridge dishes such as buckwheat with fried onions and fried mushrooms, salads, potatoes, dried fruit, beans, and other fruits and vegetables. The meal often consists of 12 dishes, representing the 12 disciples of Jesus. Vzvar is served at the end of the meal, which is a sweet drink made from dried fruit and honey boiled in water.
After the meal, Orthodox Christians attend a midnight church service, which lasts until the break of day. The meal on Christmas Day breaks the vegan fast with courses like roast pork and goose, pirogi, pelmeni, or meat dumplings, aspic, and stuffed pies. For dessert, Russians enjoy fruit pies, gingerbread and honeybread cookies, called pryaniki, and fresh and dried fruit and nuts. Don't forget the Russian Christmas cookies called kozulya, made into the shape of a sheep, goat, or deer.
Christmas night begins a two-week period known as Yuletide, or Svyatki; a time for fortune-telling and caroling. Children go caroling around the neighborhood wishing their neighbors a happy new year, who reward them with cookies, sweets, and money. Many carolers wear masks and costumes to disguise themselves so they can prank those who aren't generous with their rewards. Young girls try reading their fortunes in tea leaves, mirrors, candle wax, and barn noises to name a few. Much of the fortune-telling has to deal with finding out who "Mr. Right" will be.


Trip SavvyChristmas in Russia
Most widely celebrated on Jan. 7 because the Russian Orthodox Church adheres to the Julian calendar, which is 13 days behind the Gregorian calendar. Preceding the Russian Orthodox Christmas, New Year's Day is on Jan. 1 and is often considered the more important holiday.It is also not uncommon for Russians to observe two Christmases and even two New Year's celebrations; the first Christmas is observed on Dec. 25, and the second New Year's is observed on Jan. 14. Any public trees-like the Christmas tree in Moscow's Red Square-serve as a symbol of the New Year.
Russian Christmas Religious Observances
During much of the 20th century as a Communist, atheist country, Russia was banned from publicly celebrating Christmas. Because so many Russians identified as atheists, the religious observance of Christmas faded out of fashion. However, since the Soviet Union fell in 1991, Russians are increasingly returning to religion, primarily Russian Orthodoxy. The number of people celebrating Christmas as a religious holiday continues to grow.Some Orthodox Christian traditions in Russia mimic Christmas traditions in other parts of Eastern Europe. As is the custom in Poland, in Russia, people will cover their floors and tables in hay to represent baby Jesus's manger. A white tablecloth is then laid out to symbolize the clothes Jesus was swaddled in. Over the holiday season, Russians may also fast; this fast is to be broken at the appearance of the first star in the sky on Christmas Eve.
A Christmas church service, which happens the night of Christmas Eve, is attended by Orthodox church members. Even President Vladimir Putin and Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev have begun attending Moscow's solemn, beautiful services.
Christmas Foods
The Christmas Eve meal concludes the Nativity Fast; it is typically meatless and can be made up of twelve dishes to represent the twelve apostles. Lenten bread, dipped in honey and garlic, is shared by all family members at this festive gathering. Kutya is a concoction of grains and poppy seeds sweetened with honey; it is served as one of the main dishes of the Christmas feast. Vegetarian-style borscht, or solyanka, is a salty stew that may also be filled with salads, sauerkraut, dried fruit, potatoes, and beans.The Christmas day meal may feature a main course of pork, goose, or another meat dish. This is accompanied by various side dishes such as aspic, stuffed pies, and desserts in various forms.
The Russian Santa Claus
The Russian Santa Claus is named Ded Moroz, or Father Frost. On New Year's Eve, he places presents for children under the New Year tree (as opposed to a Christmas tree). Snegurochka accompanies him, a snow maiden said to be his granddaughter. He carries a staff; dons a red, blue, silver, or gold coat lined with white fur; and wears valenki, traditional felt boots made of wool. Unlike Santa, Ded Moroz is tall and thin-and instead of traveling via sleigh, he gets around Russia by taking a troika, a vehicle led by three horses.To see Ded Moroz for yourself, head to any major Russian city over the holiday season. For a truly spectacular Christmas celebration with Old Man Frost, check out Moscow's Russian Winter Festival, where you can feast on bagels and jam, goggle at gigantic ice sculptures, and ride a troika.
Russian Christmastide
Svyatki-Russian Christmastide-follows Christmas and is two weeks closely associated with the pagan traditions of fortune telling and caroling. Svyatki lasts until Jan. 19, when Epiphany is celebrated. This day marks Jesus's baptism, and people honor the occasion by diving into the country's icy rivers and lakes.Christmas Gifts From Russia
If you are looking for Christmas gifts from Russia, consider buying nesting dolls and Russian lacquer boxes. In Moscow, you can find them in Izmaylovo Market or in Revolution Square during the Russian Winter Festival. You should also be able to find them in most-if not all-souvenir shops throughout the country. Don't have space in your carry-on? You can also purchase these beloved gifts online.


Culture TripDed Moroz
Every year, a snowy bearded man visits well behaved children, bringing with him gifts and festive seasonal cheer. In Russia, he goes by Grandfather Frost, or Ded Moroz, and he lives in the north of the nation. Anticipation can be such a killer, so if you can't wait for him to come to you, consider paying him a visit instead.Who is Grandfather Frost?
Grandfather Frost is Russia's fur-cloaked and red-robed Father Christmas equivalent. In Russia, the end-of-year festivities hinge on the New Year rather than Christmas, and so each year he puts gifts under the New Year's tree for children. According to legend, he is the 2,000-year-old Slavic wizard of winter. He predates Christianity in Russia, and tales from this era say he is the son of the pagan god of earth and the underworld, Veles, and Mara, the ancient goddess of Spring. However, Slavic mythology claims he is a demon.Who is Snegurochka?
Snegurochka, the Snow Maiden, is Grandfather Frost's helper and first appeared in 19th-century Russian folklore. Some fables claim that two peasants who desperately wanted a child made her out of snow, and she miraculously came to life. In another story, she was the goddaughter, or sometimes daughter or granddaughter, of Grandfather Frost. Less poetically, when the Soviet Union formed and banned religious celebrations, Grandfather Frost was still permitted to make his annual rounds. It was in these early Soviet days that the Snow Maiden came to be known as his helper.Is Grandfather Frost Nice?
Don't mistake Grandfather Frost for a benign jolly fat Santa. Although the old man loves to give presents to well behaved and kind children who work hard and listen to their parents, he will swiftly punish naughty kids. In fact, the old man used to be a bit of a brute. Legend has it he used to kidnap little children and hold them for ransom. People would feed him bowls of sweet porridge so he wouldn't freeze their plants. Nikolai Nekrasov, a 19th-century poet, once wrote a tale in which Grandfather Frost killed a widow and orphaned her children. So, no, Grandfather Frost isn't always nice.Has He Been Effected by Sovietism?
Despite religious suppression under the Communist regime, Old Man Frost was permitted as a celebratory symbol during Soviet times. Technically not a religious character, he drew the festive season's focus away from Christmas and religion and towards the secular New Year. When the Union collapsed, several of the previously Christian post-Soviet states, such as Ukraine and Bulgaria, reclaimed their religious freedoms and chose to celebrate the season with more religious characters instead. The Islamic republics of Tajikistan and Uzbekistan have either banned or encouraged their media to reduce Grandfather Frost's presence, in an effort to preserve their religious heritage.Where does Grandfather Frost Live?
He lives in Veiky Ustyug, a sleepy little town in north-west Russia that revels in its most famous resident. Legend says that this is where Grandfather Frost starts his annual journey, and in 1999 it officially became his residence. The town boasts several museums in his honour, which showcase festive trinkets and costumes. There's also a theme park, and people can visit the old man's house all year round to meander down the Path of Fairy Tales, visit his magic school and even see a few reindeer roaming around.



Reddit r/AskARussianWhat is Christmas like in Russia?
American here. Other than that the Orthodox Church observes Christmas on January 7 instead of December 25, I know very little about how Russians celebrate Christmas. Would love to hear about your traditions.
- Who knows - never met anyone who do it.
- Early in the morning my father drives up to the church, does the praying and stuff, then he gets the "saint water" and drives back home. Rest of the day goes like a usual January weekend - visiting relatives, making sure everyone is doing fine.
- There is a Nativity fast (and it is very basic without any additional fluff, not like Advent) before it. Then there is a night liturgy (that is very special and unusual one). After it parishioners go home for a feast with family and/or friends (around 02:30-03:30 in my experience). The day after it is usually a time to visit other orthodox friends to finish the feasy, exchange presents and other such things. Maybe 10% of russians are religious enough to celebrate it fully, maybe even less.
- Usually we don't. Christmas wasn't celebrated en masse under the communists, for a time being totally banned. Instead they adapted most of the Christmas traditions for the New Year, making it into a secular alternative to Christmas (although the tradition of celebrating New Year had already existed since at least Peter the Great).
New Year traditions are fairly simple - you come together with your family, there's always a big trough of Olivye salad present, mandarins, quite often champagne. For children, gifts are left under the fir tree, though adults usually just exchange them outright. It's pretty common to turn on the TV to listen to the President's speech, about how difficult the year has been and all that. At the very least to hear the Kremlin's clock on Spasskaya tower ring out.
Leading up to this more private, family part of the holiday there are often public events in schools and kindergartens, sometimes a few days prior. There's a bit of ceremony there, with the kids calling out for Grandfather Frost and his granddaughter Snegurochka to come by, and then getting some small present from them.
The actual Christmas is only celebrated by the religious Christians. Sure, it's still a state holiday and you get a day off (as you do with the entire week between the New Year and Christmas), but it's not celebrated by many. Whether or not there are specific traditions there, I don't really know. I know services are held in churches, and I'm guessing there's some ceremony there, but not being a believer, I never really found out what it was about.
- For most, it's just the second New Year, a family holiday, when it's customary to visit friends and relatives. For believers, it is a great holiday, preceded by a 40-day advent. On the night before Christmas, special services will be held in all churches. The liturgy in the Cathedral of Christ the Savior is shown live on TV.
- Most people celebrate like the second new year, but less solemnly or don't celebrate at all. The rest go to church. In fact, Christmas was replaced by the new year under the Communists, so their celebration is no different, with the exception of the religious component
- We don't. NY is a huge thing, we exchange presents and so on. But on Christmas most of the people do nothing. In my family there's a cute and old tradition to get together and cook dumplings (chatting, drinking and laughing of course)

WIKIPEDIAChristmas in Russia
In the Russian Orthodox Church, is a holiday commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ. It is celebrated on 25 December in the Gregorian calendar and 7 January in the Julian calendar followed by the Eastern Orthodox Church. It is considered a high holiday by the church, one of the 12 Great Feasts, and one of only four of which are preceded by a period of fasting. Traditional Russian Christmas festivities start on Christmas Eve, which is celebrated on 6 January .Christmas was largely erased from the Russian calendar for much of the 20th century due to the Soviet Union's anti-religious policies, but many of its traditions survived, having been transplanted to New Year's Day. Although Christmas was re-established as a holiday in the 1990s after the collapse of the Soviet Union, it is still eclipsed by New Year's Day, which remains the most important Russian holiday.
On Christmas Eve (6 January), there are several long church services, including the Royal Hours and Vespers combined with the Divine Liturgy. The family will then return home for the traditional Christmas Eve (Holy Supper), which consists of 12 dishes, one to honour each of the Twelve Apostles. Devout families will then return to church for the All Night Vigil. Then again, on Christmas Morning, they return to attend the Morning Divine Liturgy of the Nativity. Since 1992, Christmas has become a national holiday in Russia as part of the ten-day holidays at the start of the new year.
Principal dishes on the Christmas table in old Russia included roasted pig, stuffed pig's head, roasted meat chunks, jelly (kholodets), and aspic. Christmas dinner also included many other meats: goose with apples, sour cream hare, venison, lamb, whole fish, etc. The abundance of fried and baked meats, whole baked chicken, and fish on the festive table was associated with features of the Russian oven, which allowed successful preparation of large portions.
Finely sliced meat and pork was cooked in pots with semi-traditional porridge. Pies were indispensable dishes for Christmas, as well as other holidays, and included both closed and open style pirogi (pirozhki, vatrushkas, coulibiacs, kurnik, saechki, shangi), kalachi, cooked casseroles, and blini. Fillings of every flavor were included (herbal, vegetable, fruit, mushrooms, meat, fish, cheese, mixed).
Sweet dishes served on the Russian Christmas table included berries, fruit, candy, cakes, angel wings, biscuits, honey. Beverages included drinking broths (kompot and sweet soups, sbiten), kissel, and, from the beginning of the 18th century, Chinese tea.
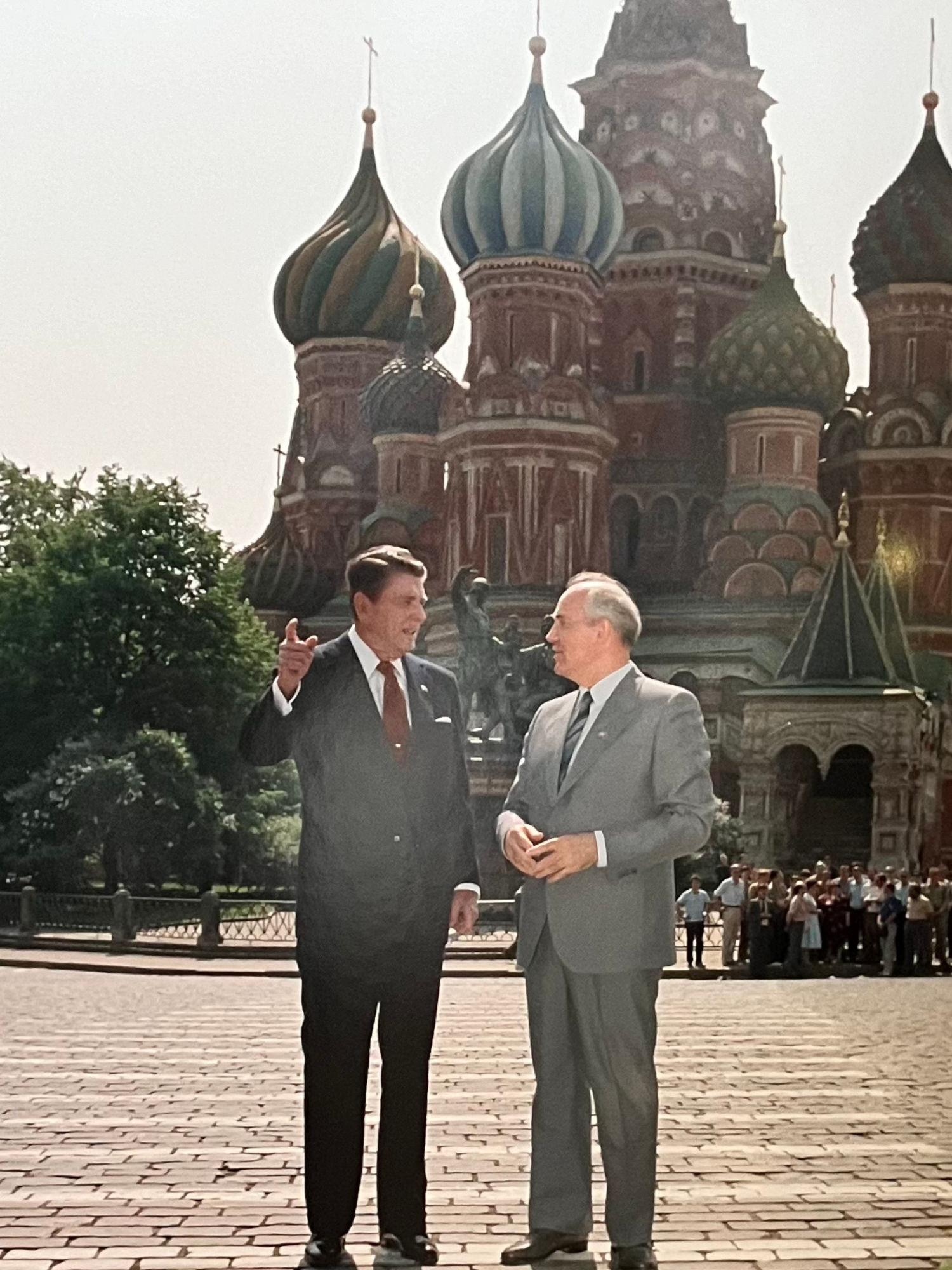


Reagan and Gorbachev stand and talk in Red Square; St. Basil's Cathedral is in the background; President Reagan attended Summit meeting with General Secretary Gorbachev and exchanged ratifications of INF Treaty.
Reagan's Daily DiaryTuesday, May 31, 1988
Nancy off early on her visit to Leningrad. My usual beginning in the ice house thats what I call the bug proof box we can hold our meetings in. Then my 3rd meeting with Gorbachev & again we got along well-it was a 1 on 1. Then he took me for a brief walk around the Kremlin grounds before we went back for the plenary meeting. Following meeting we attended the Shultz, Shevardnadze signing ceremony of some bilateral agreements-we’re up to about 47 of those now. Then it was a luncheon with a group of cultural & art community members at the House of Writers Assn. I spoke to them about the need for freedom of the arts. Then a couple of hours of free time (homework) and over to St. U. of Moscow where I addressed & took Q’s. from more than 1,000 students. Later met with 35 American Faculty members there on exchange.Before day was over Gorbachev walked me out into Red Square. It is quite a sight-the expanse is so great it is really something to see. We stopped & talked with several groups of people who were there.
Tonite our dinner for the Gorbachevs-very pleasant & entertainment by our famous American jazz artists quartet.
Key Facts
- President Reagan and General Secretary Gorbachev attend a private meeting and discuss mutual interests.
- President Reagan addresses a group at the House of Writers.
- President Reagan addresses and takes questions from graduating students of Moscow University.
RONALD REAGAN Remarks at the Opening Ceremony of the Soviet-United States Summit Meeting in MoscowMay 29, 1988
The General Secretary. Esteemed Mr. Ronald Reagan, President of the United States of America; esteemed Mrs. Nancy Reagan: On behalf of the people and Government of the Soviet Union, I extend to you my sincere greetings on the occasion of your visit. Welcome!
It is now almost 6 months since our meeting in Washington, which went down in history as a major milestone in Soviet-American and in international relations. Now, on this return trip, you, Mr. President, have traversed the great distance that lies between our two capitals to continue our political dialog. This is a fact we duly appreciate. As this is our fourth meeting, we can already make some meaningful assessments. As we see it, long-held dislikes have been weakened; habitual stereotypes stemming from enemy images have been shaken loose. The human features of the other nation are now more clearly visible. This in itself is important, for at the turn of the two millenniums, history has objectively bound our two countries by a common responsibility for the destinies of mankind. The peoples of the world and, in the first place, the Soviet and the American people welcome the emerging positive changes in our relationship and hope that your visit and talks here will be productive, providing a fresh impetus in all areas of dialog and interaction between our two great nations.
You and I are conscious of our two peoples' longing for mutual understanding, cooperation, and a safe and stable world. This makes it incumbent upon us to discuss constructively the main aspects of disarmament: the set of issues related to 50-percent cuts in strategic offensive arms, while preserving the 1972 ABM treaty; problems of eliminating chemical weapons; reductions in armed forces and conventional armaments in Europe; cessation of nuclear testing. The world is also looking to us, Mr. President, for responsible judgments on other complex issues of today, such as the settlement of regional conflicts; improving international economic relations; promoting development; overcoming backwardness, poverty, and mass diseases; and humanitarian problems.
And of course, we shall discuss bilateral relations. Our previous meetings have shown that constructive Soviet-U.S. relations are possible. The treaty on intermediate and shorter range missiles is the most impressive symbol of that. But even more complex and important tasks lie ahead. And so, Mr. President, you and I still have a lot of work to do. And it is good when there is a lot of work to be done and people need that work. We are ready to do our utmost in these coming days in Moscow.
Mr. President, you and Mrs. Reagan are here on your first visit to the Soviet Union, a country which you have so often mentioned in your public statements. Aware of your interest in Russian proverbs, let me add another one to your collection: "It is better to see once than to hear a hundred times." Let me assure you that you can look forward to hospitality, warmth, and good will. You will have many meetings with Soviet people. They have a centuries-old history behind them. They love their land and take pride in their accomplishments. They resent things that are presently standing in their way, and they are heatedly discussing how their country can best progress. They are full of plans for the future.
Being ardent patriots, Soviet people are open to friendship and cooperation with all nations. They harbor sincere respect for the American people and want good relations with your country. Here, within the walls of the ancient Kremlin, where one feels the touch of history, people are moved to reflect over the diversity and greatness of human civilization. So, may this give greater historical depth to the Soviet-American talks to be held here, infusing them with a sense of mankind's shared destinies. Once again, I bid you welcome.
The President. Mr. General Secretary, Mrs. Gorbachev: Mr. General Secretary, thank you for those kind words of welcome. We've traveled a long road together to reach this moment -- from our first meeting in Geneva in November, 1985, when I invited you to visit me in Washington and you invited me to Moscow. It was cold that day in Geneva, and even colder in Reykjavik when we met the following year to work on the preparations for our exchange of visits. We've faced great obstacles; but by the time of your visit to Washington last December, although we still had to grapple with difficult issues, we had achieved impressive progress in all the areas of our common agenda -- human rights, regional issues, arms reduction, and our bilateral relations.
We signed a treaty that will reduce the level of nuclear arms for the first time in history by eliminating an entire class of U.S. and Soviet independent [intermediate-] range missiles. We agreed on the main points of a treaty that will cut in half our arsenals of strategic offensive nuclear arms. We agreed to conduct a joint experiment that would allow us to develop effective ways to verify limits on nuclear testing. We held full and frank discussions that planted the seeds for future progress.
It is almost summer; and some of those seeds are beginning to bear fruit, thanks to the hard work we have both done since our last meeting, including monthly meetings by our Foreign Ministers and the first meeting of our Defense Ministers. We have signed the Geneva accords, providing for the withdrawal of all Soviet troops from Afghanistan, and the first withdrawals have begun. We and our allies have completed technical arrangements necessary to begin implementing the INF treaty as soon as it enters into force. For the next major step in arms control, reductions in U.S. and Soviet strategic offensive arsenals, our negotiators in Geneva have produced hundreds of pages of joint, draft treaty text recording our areas of agreement, as well as those issues yet to be resolved. Our new nuclear risk reduction centers have begun their transmissions of routine notifications to reduce the risk of conflict. Our scientists are installing the equipment for our joint experiment to verify limits on nuclear testing. Our experts have held broad-ranging discussions on human rights, and important steps have been taken in that area. We have greatly expanded our bilateral exchanges since we signed our agreement in 1985. I hope you'll agree with me that more of our young people need to participate in these exchanges, which can do so much to lay the basis for greater mutual understanding in the next generation.
I could go on; the list of accomplishments goes far beyond what many anticipated. But I think the message is clear: Despite clear and fundamental differences, and despite the inevitable frustrations that we have encountered, our work has begun to produce results. In the past, Mr. General Secretary, you've taken note of my liking for Russian proverbs. And in order not to disappoint anyone on this visit, I thought I would mention a literary saying from your past, another example of your people's succinct wisdom: Rodilsiya ne toropilsiya -- It was born, it wasn't rushed.
Mr. General Secretary, we did not rush. We have taken our work step by step. And I have come here to continue that work. We both know it will not be easy. We both know that there are tremendous hurdles yet to be overcome. But we also know that it can be done because we share a common goal: strengthening the framework we have already begun to build for a relationship that we can sustain over the long term, a relationship that will bring genuine benefits to our own peoples and to the world.
Thank you, and God bless you.
NOTEThe General Secretary spoke at 2:55 p.m. in St. George's Hall at the Grand Kremlin Palace. The President spoke in English, and the General Secretary spoke in Russian. Their remarks were translated by interpreters.
WIKIPEDIAThe Russian Federation
A country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world by area, extends across eleven time zones, and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow. Saint Petersburg is Russia's second-largest city and "cultural capital". Other major urban areas in the country include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, Chelyabinsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Kazan.The East Slavs emerged as a recognized group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. The first East Slavic state, Kievan Rus', arose in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire. Rus' ultimately disintegrated, with the Grand Duchy of Moscow growing to become the Tsardom of Russia. By the early 18th century, Russia had vastly expanded through conquest, annexation, and the efforts of Russian explorers, developing into the Russian Empire, which remains the third-largest empire in history. However, with the Russian Revolution in 1917, Russia's monarchic rule was abolished and eventually replaced by the Russian SFSR-the world's first constitutionally socialist state. Following the Russian Civil War, the Russian SFSR established the Soviet Union with three other Soviet republics, within which it was the largest and principal constituent. At the expense of millions of lives, the Soviet Union underwent rapid industrialization in the 1930s and later played a decisive role for the Allies in World War II by leading large-scale efforts on the Eastern Front. With the onset of the Cold War, it competed with the United States for global ideological influence. The Soviet era of the 20th century saw some of the most significant Russian technological achievements, including the first human-made satellite and the first human expedition into outer space.
In 1991, the Russian SFSR emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union as the independent Russian Federation. A new constitution was adopted, which established a federal semi-presidential system.

- The Russian economy ranks 11th by nominal GDP, relying heavily on its abundant natural resources.
- Its mineral and energy sources are the world's largest, and its figures for oil production and natural gas production rank highly globally.
- The Russian GDP ranks 68th by per capita
- Russia possesses the largest stockpile of nuclear weapons and has the third-highest military expenditure.
- The country is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council; a member state of the G20, SCO, BRICS, APEC, OSCE, and WTO; and the leading member state of post-Soviet organizations such as CIS, CSTO, and EAEU/EEU.
- Russia is home to 30 UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
- The first human settlement on Russia dates back to the Oldowan period in the early Lower Paleolithic. About 2 million years ago, representatives of Homo erectus migrated to the Taman Peninsula in southern Russia. Flint tools, some 1.5 million years old, have been discovered in the North Caucasus. Radiocarbon dated specimens from Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains estimate the oldest Denisovan specimen lived 195–122,700 years ago. Fossils of Denny, an archaic human hybrid that was half Neanderthal and half Denisovan, and lived some 90,000 years ago, was also found within the latter cave. Russia was home to some of the last surviving Neanderthals, from about 45,000 years ago, found in Mezmaiskaya cave. The first trace of an early modern human in Russia dates back to 45,000 years, in Western Siberia.
- Russia's vast landmass stretches over the easternmost part of Europe and the northernmost part of Asia. Russia, as one of the world's only three countries bordering three oceans, has links with a great number of seas. Russia, home of over 100,000 rivers, has one of the world's largest surface water resources, with its lakes containing approximately one-quarter of the world's liquid fresh water. Lake Baikal, the largest and most prominent among Russia's fresh water bodies, is the world's deepest, purest, oldest and most capacious fresh water lake, containing over one-fifth of the world's fresh surface water.
- The size of Russia and the remoteness of many of its areas from the sea result in the dominance of the humid continental climate throughout most of the country, except for the tundra and the extreme southwest.
- Russian biodiversity includes 12,500 species of vascular plants, 2,200 species of bryophytes, about 3,000 species of lichens, 7,000–9,000 species of algae, and 20,000–25,000 species of fungi. Russian fauna is composed of 320 species of mammals, over 732 species of birds, 75 species of reptiles, about 30 species of amphibians, 343 species of freshwater fish (high endemism), approximately 1,500 species of saltwater fishes, 9 species of cyclostomata, and approximately 100–150,000 invertebrates (high endemism). Approximately 1,100 rare and endangered plant and animal species are included in the Russian Red Data Book.
- Russia, by 1993 constitution, is a symmetric federal republic with a semi-presidential system, wherein the president is the head of state, and the prime minister is the head of government. It is structured as a multi-party representative democracy, with the federal government composed of three branches: Legislative, Executive, and Judiciary.
- Russia has a market economy, with enormous natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. It has the world's ninth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the sixth-largest by PPP. The large service sector accounts for 62% of total GDP, followed by the industrial sector (32%), while the agricultural sector is the smallest, making up only 5% of total GDP.
- Russia is the world's thirteenth-largest exporter and the 21st-largest importer. It relies heavily on revenues from oil and gas-related taxes and export tariffs, which accounted for 45% of Russia's federal budget revenues in January 2022, and up to 60% of its exports in 2019.
- Roscosmos is Russia's national space agency. In 1957, the first Earth-orbiting artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, was launched. In 1961, the first human trip into space was successfully made by Yuri Gagarin. Many other Soviet and Russian space exploration records ensued. In 1963, Valentina Tereshkova became the first and youngest woman in space, having flown a solo mission on Vostok 6. In 1965, Alexei Leonov became the first human to conduct a spacewalk, exiting the space capsule during Voskhod 2. Russia had 172 active satellites in space in April 2022, the world's third-highest.
- According to the World Tourism Organization, Russia was the sixteenth-most visited country in the world, and the tenth-most visited country in Europe, in 2018, with over 24.6 million visits.
- Russia is one of the world's most sparsely populated and urbanised countries, with the vast majority of its population concentrated within its western part. It had a population of 144.7 million as of the 2021 census (excluding Crimea and Sevastopol). Russia is the most populous country in Europe, and the world's ninth most populous country.
- Russian is the official and the predominantly spoken language in Russia. It is the most spoken native language in Europe, the most geographically widespread language of Eurasia, as well as the world's most widely spoken Slavic language. Russian is one of two official languages aboard the International Space Station, as well as one of the six official languages of the United Nations.
- Russia largest religion is Eastern Orthodox Christianity.
- Russia has an adult literacy rate of 100%.
- Russian cuisine has been formed by climate, cultural and religious traditions, and the vast geography of the nation; and it shares similarities with the cuisines of its neighbouring countries. Crops of rye, wheat, barley, and millet provide the ingredients for various breads, pancakes and cereals, as well as for many drinks. Bread, of many varieties, is very popular across Russia. Flavourful soups and stews include shchi, borsch, ukha, solyanka, and okroshka. Smetana (a heavy sour cream) and mayonnaise are often added to soups and salads. Pirozhki, blini, and syrniki are native types of pancakes. Beef Stroganoff,: 266 Chicken Kiev,: 320 pelmeni, and shashlyk are popular meat dishes. Other meat dishes include stuffed cabbage rolls (golubtsy) usually filled with meat. Salads include Olivier salad, vinegret, and dressed herring.
- Russia's national non-alcoholic drink is kvass, and the national alcoholic drink is vodka; its production in Russia (and elsewhere) dates back to the 14th century. The country has the world's highest vodka consumption, while beer is the most popular alcoholic beverage. Wine has become increasingly popular in Russia in the 21st century. Tea has been popular in Russia for centuries.
- Football is the most popular sport in Russia. Ice hockey is very popular in Russia, and the Soviet national ice hockey team dominated the sport internationally throughout its existence. Bandy is Russia's national sport, and it has historically been the highest-achieving country in the sport. The Russian national basketball team won the EuroBasket 2007, and the Russian basketball club PBC CSKA Moscow is among the most successful European basketball teams. The annual Formula One Russian Grand Prix was held at the Sochi Autodrom in the Sochi Olympic Park, until its termination following the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022. Historically, Russian athletes have been one of the most successful contenders in the Olympic Games.
EtymologyThe word Rus' is derived from the Rus' people, who were a Swedish tribe, and where the three original members of the Rurikid dynastry came from. The Finnish word for Swedes, ruotsi, has the same origin. The word Russia is a Medieval Latin name for Rus', a medieval state populated primarily by the East Slavs. In modern historiography, this state is usually denoted as Kievan Rus' after its capital city.