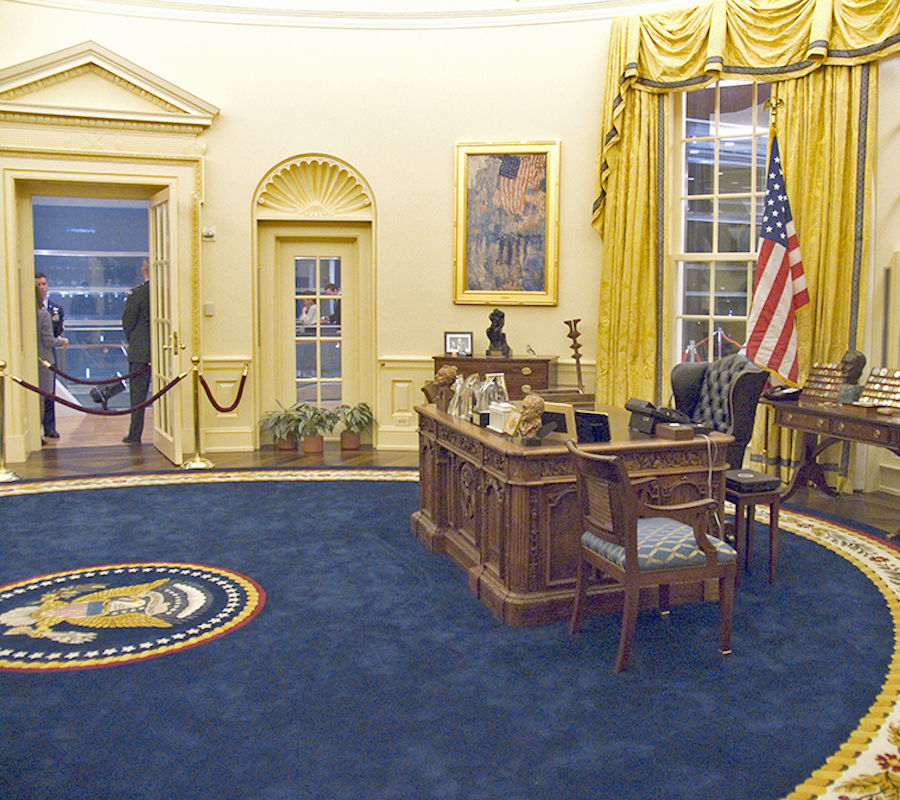
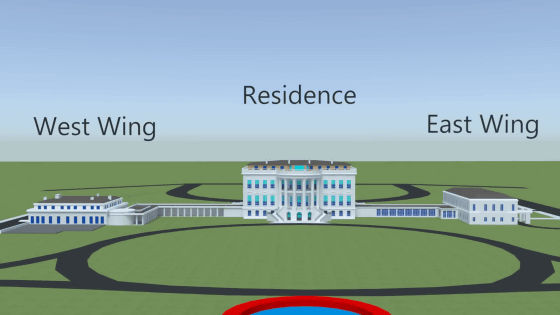
The White House
Just as it did when it was first completed over 200 years ago, the White House still houses the president's family as well as offices for their top staff (although today, many more "White House staff" members work in the Eisenhower Executive Office Building across the street).The chief usher is in charge of keeping the house running smoothly. He has a staff of 90 workers to assist him: a head housekeeper, five chefs, and numerous maids, butlers, carpenters, plumbers, gardeners, and engineers. The Residence is 170 feet wide by 85 feet deep and 58 feet high.
The White House has:
- A main residence and architectural wings on the east and west sides
- 4 stories, plus a basement and sub-basement
- 55,000 square feet of floor space (67,000 square feet including the wings)
- 132 rooms and 35 bathrooms
- 412 doors
- 147 windows
- 28 fireplaces
- 8 staircases
- 3 elevators (main, pantry, and a lower-levels elevator under the Grand Staircase)
- several gardens
- a tennis court
- a basketball court
- a putting green
- a bowling alley
- a movie theater
- a jogging track
- a swimming pool

https://www.google.com/maps/place/The+White+House
https://www.google.com/maps/place/National+Mall

Looking at the South Lawn then the WH in the distance. Drive by photo taken from Constitution Avenue.

 Was It Always Called the White House?:
Was It Always Called the White House?:The stone exterior of the building was first painted with a lime-based whitewash in 1798 to protect it from the elements and freezing temperatures. According to the White House Historical Association, the "White House" moniker began to appear in newspapers before the War of 1812.
But it was President Theodore Roosevelt, who, in 1901, designated the official name of the residence of the U.S. president to be the White House. (Previous names included the Presidents' House, the Executive Mansion, the Presidential Palace and the Presidential Mansion.) It also commonly goes by "The People's House."
https://www.history.com/news/white-house-history-facts-presidents

Series 2004 $20 bill compared to series 1985 - notice how one is the front of the white house and the other is the back of it.
Portico: - A roof supported by columns at regular intervals, normally attached as a porch to a building. The North Portico at the main entrance to the White House was installed around 1830 to provide shelter to guests arriving by horse drawn carriage
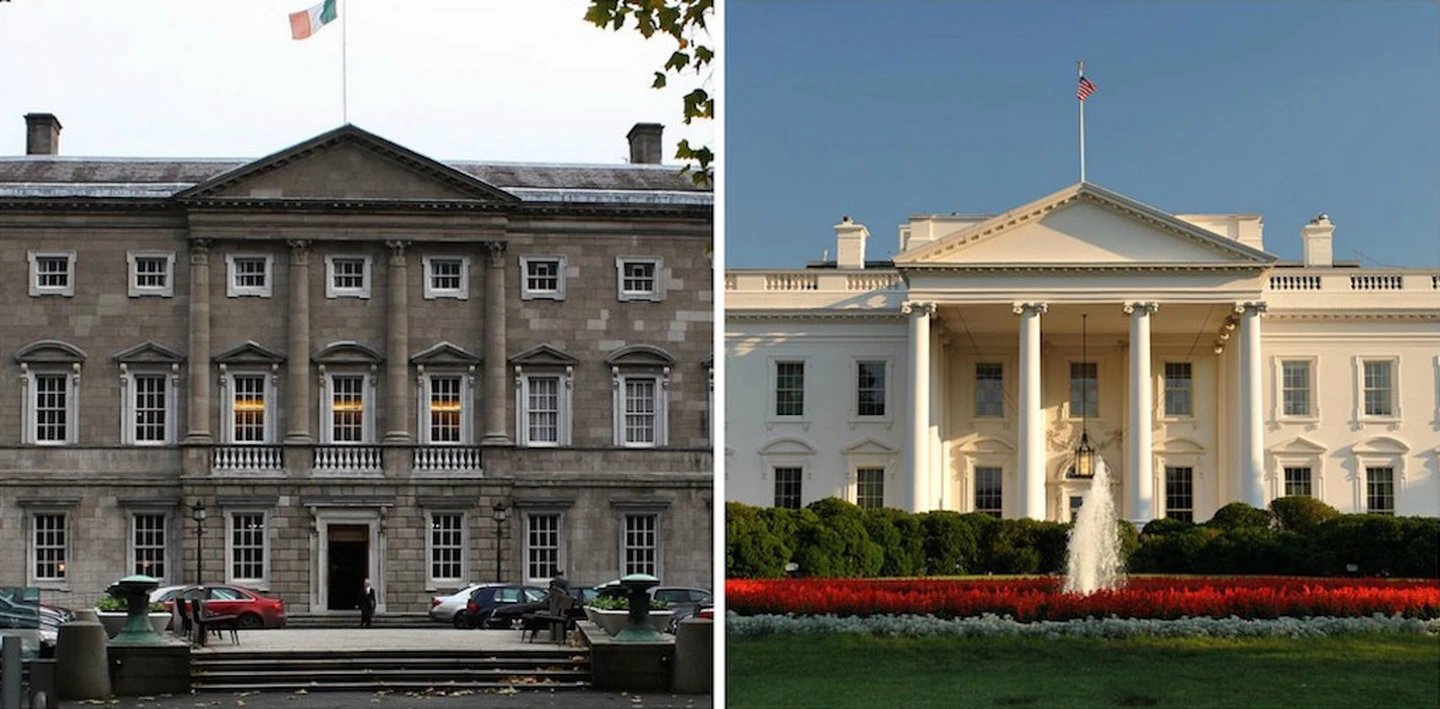

The White House building - in particular, its upper floors - has been proven to have been based on the design of Dublin's Leinster House. Built from 1745 to 1748, the Georgian palace of the first Duke of Leinster was, at that time, one of Ireland's grandest homes.
Since 1922 it has functioned as the seat of the Oireachtas, Ireland's modern-day parliament.
The White House: is often used as a figure of speech referring to the Executive Branch of the government.

How the U.S. Government Is Organized:
- Legislative - Makes laws (Congress, comprised of the House of Representatives and Senate)
- Executive - Carries out laws (president, vice president, Cabinet, most federal agencies)
- Judicial - Evaluates laws (Supreme Court and other courts)
Each of the 3 can change acts of the other branches:
- The president can veto legislation created by Congress and nominates heads of federal agencies.
- Congress confirms or rejects the president's nominees and can remove the president from office in exceptional circumstances.
- The Justices of the Supreme Court, who can overturn unconstitutional laws, are nominated by the president and confirmed by the Senate.
This ability of each branch to respond to the actions of the other branches is called the system of checks and balances
Executive Branch:
The executive branch carries out and enforces laws.
It includes the president, vice president, the Cabinet, executive departments, independent agencies, and other boards, commissions, and committees.
The President:
The president leads the country:
- The head of state
- Leader of the federal government
- Commander in Chief of the United States armed forces
The president serves a four-year term and can be elected no more than two times.
The Vice president:
The vice president supports the president. If the president is unable to serve, the vice president becomes president.
The vice president can be elected and serve an unlimited number of four-year terms as vice president, even under a different president.
The Cabinet
Cabinet members serve as advisors to the president.
They include the vice president, heads of executive departments, and other high-ranking government officials.
Cabinet members are nominated by the president and must be approved by a simple majority of the Senate (51 votes if all 100 Senators vote).
 The Cabinet:
The Cabinet:The Cabinet's role is to advise the President on any subject he or she may require relating to the duties of each member's respective office.
























The Chief of Staff:
Responsible for directing, managing and overseeing all policy development, daily operations, and staff activities for the President.
 Executive Office of the President:
Executive Office of the President:The Executive Office of the President (EOP) was created in 1939 by President Franklin D. Roosevelt.
- Council of Economic Advisers
Established by Congress in 1946, the Council of Economic Advisers is charged with advising the President on economic policy based on data, research, and evidence. The CEA is composed of three members, including a Chair who is appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate. - Council on Environmental Quality
CEQ, which was created in 1969 by the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), advises the President and develops policies on climate change, environmental justice, federal sustainability, public lands, oceans, and wildlife conservation, among other areas. - Domestic Policy Council
Domestic policy staff have existed in the White House since the 1960s. President Lyndon B. Johnson assigned a senior-level aide to organize staff and develop domestic policy. In 1970, President Richard M. Nixon issued an executive order that created the Office of Policy Development, a large White House office with jurisdiction over economic and domestic policy. President William J. Clinton split the office, forming the current Domestic Policy Council and the National Economic Council. - Gender Policy Council
The GPC was established by President Biden. - National Economic Council
NEC was established in 1993. The NEC has four key functions:- Coordinate policy-making for domestic and international economic issues
- Give economic policy advice to the President
- Ensure that policy decisions and programs are consistent with the President's economic goals
- Monitor implementation of the President's economic policy agenda
- National Security Council
The National Security Council was established by the National Security Act of 1947. The NSC is chaired by the President. Its regular attendees are the Vice President, the Secretary of State, the Secretary of the Treasury, the Secretary of Defense, the Secretary of Energy, the Attorney General, the Secretary of Homeland Security, the Representative of the United States of America to the United Nations, the Administrator of the U.S. Agency for International Development, the Chief of Staff to the President, and the Assistant to the President for National Security Affairs. The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is the military advisor to the Council, and the Director of National Intelligence is the intelligence advisor. - Office of Intergovernmental Affairs
Serves to engage State, local, and Tribal governments, in addition to elected officials across Puerto Rico and our island communities. - Office of Management and Budget
OMB carries out its mission through five main functions:- Budget development and execution
- Management, including oversight of agency performance, procurement, financial management, and information technology
- Coordination and review of all significant Federal regulations from executive agencies, privacy policy, information policy, and review and assessment of information collection requests
- Clearance and coordination of legislative and other materials, including agency testimony, legislative proposals, and other communications with Congress, and coordination of other Presidential actions
- Clearance of Presidential Executive Orders and memoranda to agency heads prior to their issuance
- Office of National Drug Control Policy
ONDCP leads and coordinates the nation's drug policy through:- Developing and overseeing implementation of the National Drug Control Strategy
- Developing and overseeing implementation of the National Drug Control Budget
- Administering High Intensity Drug Trafficking Areas and Drug-Free Communities grant programs
- Office of Public Engagement
Build and maintain the transparent, responsible, and accountable government - Office of Science and Technology Policy
Congress established the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) in 1976. OSTP leads efforts across the Federal government to develop and implement sound science and technology policies and budgets. - Office of the United States Trade Representative
USTR was created in 1962. With more than 200 committed public servants, USTR meets with governments, business groups, legislators and the general public to gather input on trade issues and discuss the President's trade policy positions. Offices in Washington, Geneva, and Brussels. - National Space Council
The NSpC was established by law as part of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Authorization Act of 1989. The Council was not operational from 1993-2017. The NSpC is aided by a staff from the Executive Office of the President led by a civilian Executive Secretary. It is also supported by the Users Advisory Group, a Federal Advisory Committee consisting of outside experts from industry, academia, and other non-Federal organizations.
https://www.whitehouse.gov/administration/executive-office-of-the-president
District of Columbia (DC): - a federal district carved out of neighboring states Maryland and Virginia.
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United StatesThe White House:
- It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington DC
- It has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800.
- The residence was designed by Irish-born architect James Hoban in the neoclassical style. Hoban modeled the building on Leinster House in Dublin.
- Construction using Aquia Creek sandstone painted white took place between 1792 and 1800.
- When Thomas Jefferson moved into the house in 1801, he (with architect Benjamin Henry Latrobe) added low colonnades on each wing that concealed stables and storage.
In 1814, during the War of 1812, the mansion was set ablaze by the British Army in the Burning of Washington, destroying the interior and charring much of the exterior. Reconstruction began almost immediately, and President James Monroe moved into the partially reconstructed Executive Residence in October 1817.
- The addition of the semi-circular South portico in 1824 and the North portico in 1829.
- Because of crowding within the executive mansion itself, President Theodore Roosevelt had all work offices relocated to the newly constructed West Wing in 1901.
- Eight years later, in 1909, President William Howard Taft expanded the West Wing and created the first Oval Office, which was eventually moved as the section was expanded.
- In the main mansion, the third-floor attic was converted to living quarters in 1927 by augmenting the existing hip roof with long shed dormers.
- A newly constructed East Wing was used as a reception area for social events; Jefferson's colonnades connected the new wings.
- The East Wing alterations were completed in 1946, creating additional office space.
By 1948, the residence's load-bearing exterior walls and internal wood beams were found to be close to failure. Under Harry S. Truman, the interior rooms were completely dismantled and a new internal load-bearing steel frame was constructed inside the walls. On the exterior, the Truman Balcony was added.The modern-day White House complex includes the Executive Residence, the West Wing, the East Wing, the Eisenhower Executive Office Building (the former State Department, which now houses offices for the president's staff and the vice president) and Blair House, a guest residence.
Executive Residence is made up of six stories: the Ground Floor, State Floor, Second Floor, and Third Floor, as well as a two-story basement.









