

- Snout
- Jowl
- Ear
- Neck
- Clear Plate
- Boston Butt
- Picnic Ham
- Back Fat
- Loin
- Spar Ribs
- Bacon
- Legs or Ham
- Hock
- Hock


- Pigs talk! They communicate constantly with each other and more than 20 different vocalizations have been identified.
- Pigs are highly intelligent and very social. In a group, pigs will snuggle close and prefer to sleep nose-to-nose.
- Pigs will eat almost anything
- Pigs genetic makeup is very close to humans. Their stem cells are used by scientists to research cures for human diseases.
- Adult pigs can run at speeds of up to 11 mph or a 7 minute mile.
- Pigs drink up to 14 gallons of water everyday.
- Pigs have hardly any sweat glands. They love to cool themselves off by wallowing in the mud.
- Pigs have 15,000 taste buds! Humans have 9,000.
- A pig's squeal can be as loud as 115 decibels - 3 decibels higher than the sound of a supersonic airliner.
- Mother pigs sing to their young while nursing.
- On the uninhabited Bahamian Island of Big Major Cay, pigs swim. A population of wild aquatic swine rules the island and many have taken to swimming out to boats for treats.
- Pigs have a tremendous sense of smell.
- Newborn piglets can recognize their own names by the time they are 2 weeks old.


- Hampshire
- Chester White
- Poland China
- Landrace
- Berkshire
- Yorkshire
- Duroc
- Spotted
By Gianna P.


Ear tagging is used to identify each pig.
- Right Ear
The right ear is used for litter marks, and all pigs in the same litter must have the same ear notches on this ear. - Left Ear
The left ear is used for notches to individual pig number in the litter. Each pig will have different notches.


- Gilt A female pig that has never given birth
- Sow A female pig that hase given birth
- Boar A male pig
- Barrow A castrated male pig


- Exercising and Practicing
Some tips to keep in mind when starting to work with your animal:- Anything you do with the animal at home will relate to what your animal does in the show ring.
- Use the same type driving tool at home as you plan to use in the show ring.
- Mix up your exercise pattern, animals can fall into a rut of doing the same thing over and over again.
- Once your animal is easily controlled with your driving tool it is a good practice technique to put up obstacles to walk your animal around.
- A well-groomed animal is essential for the showing. This includes the pig being clean, free of scratches, sunburns and other blemishes. Also, having a neatly clipped pig is important so both of you look sharp.
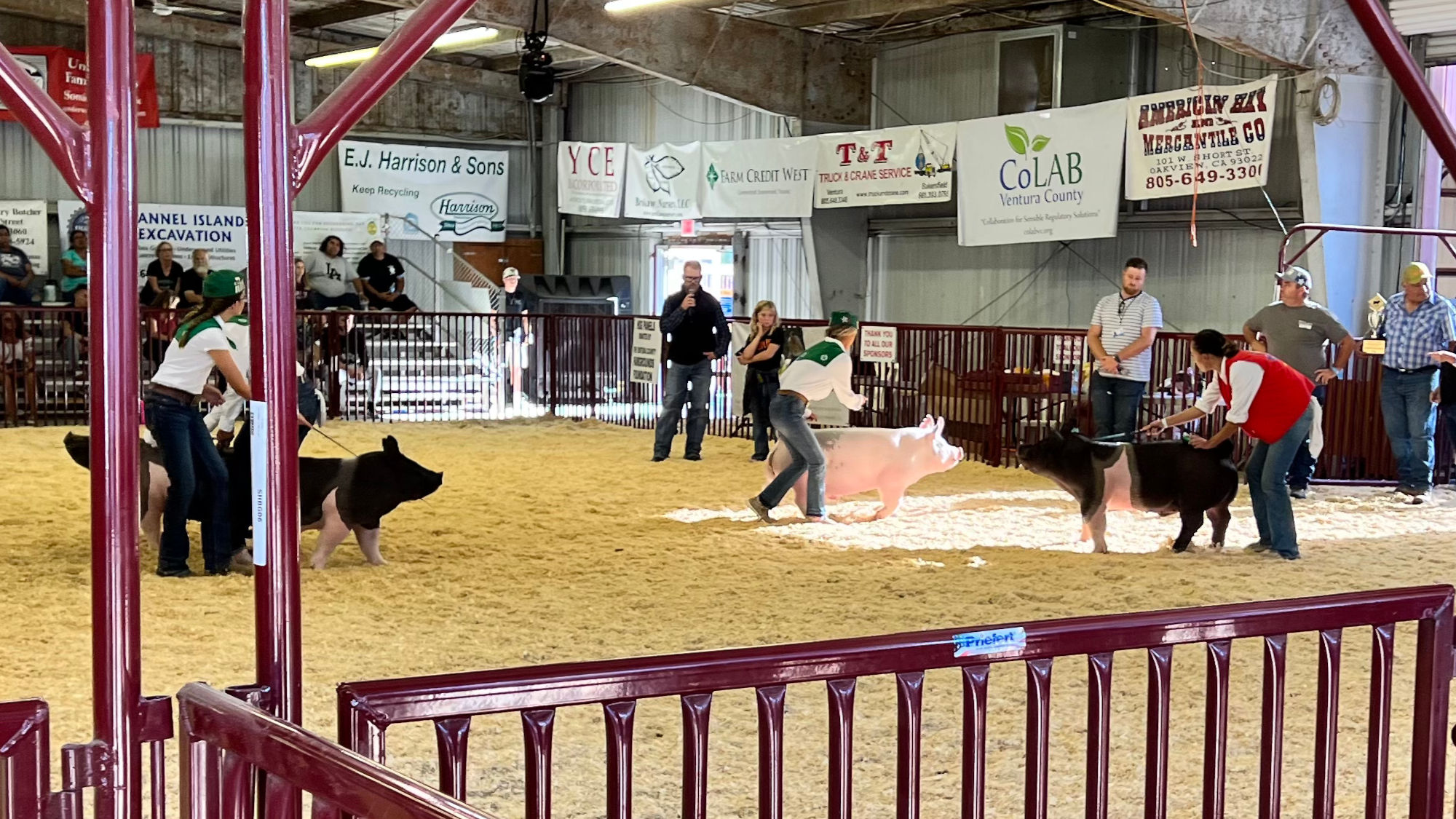
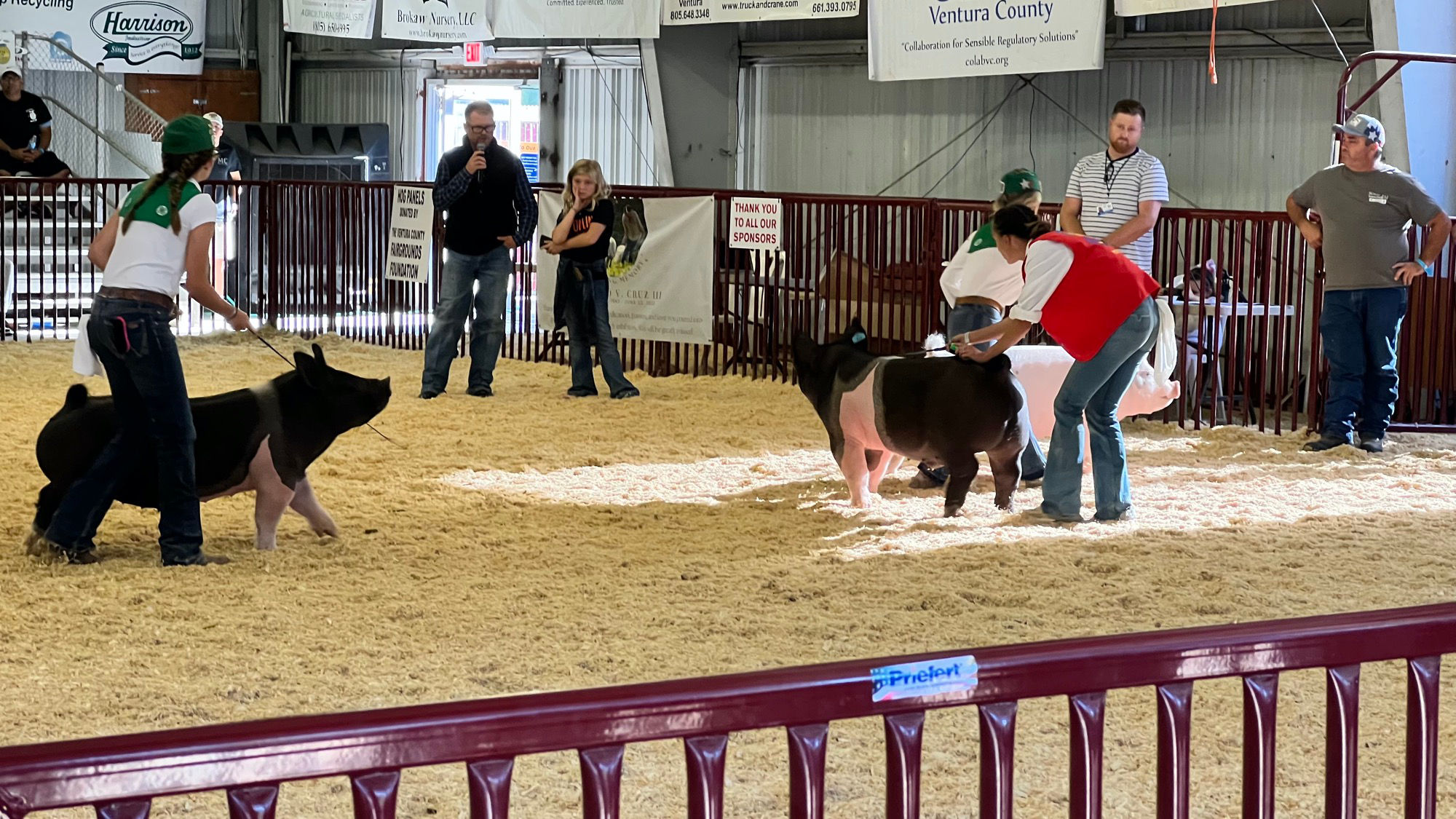
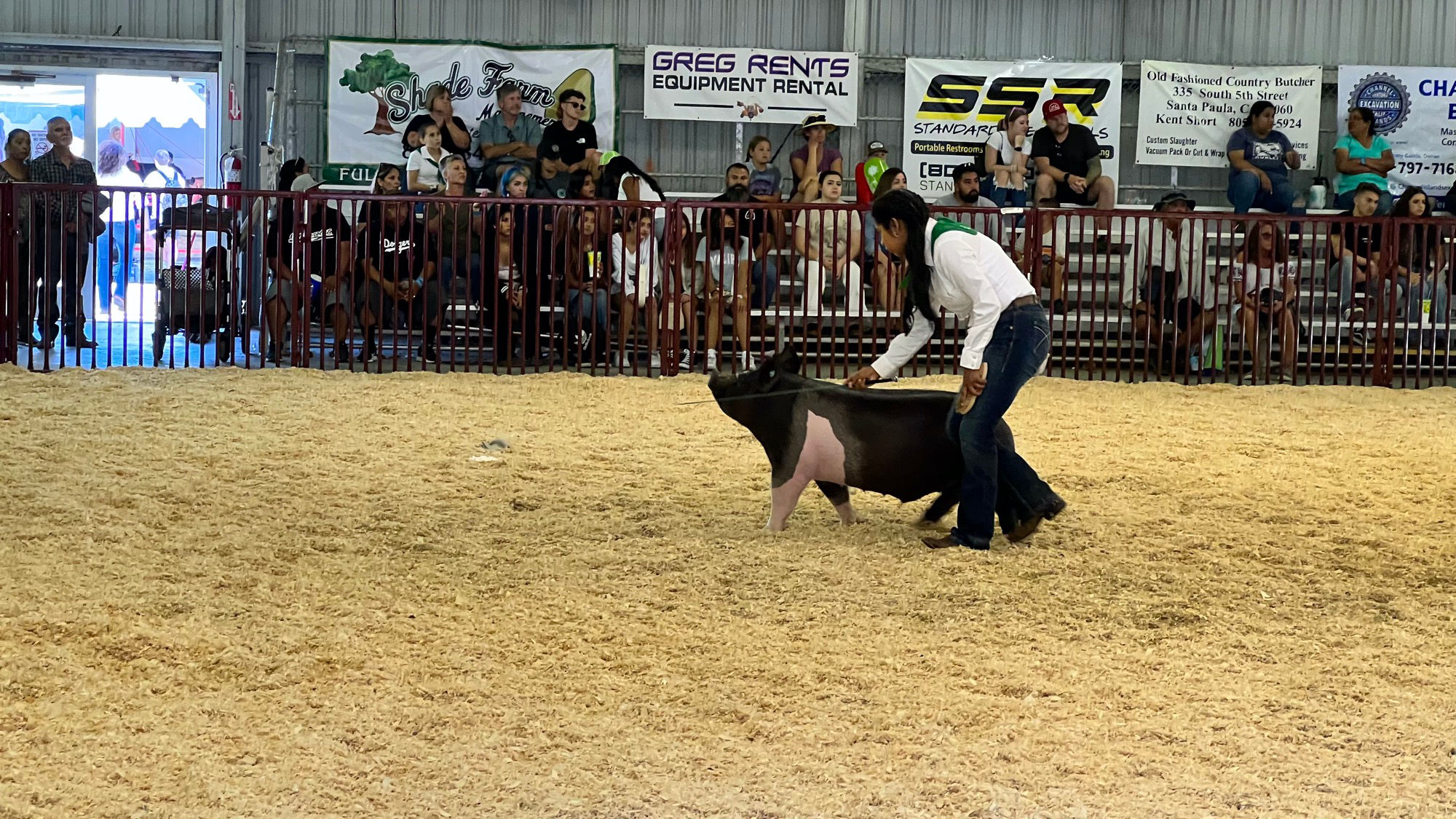
- Showing Your Swine
When you enter the show ring, stay calm. Once your animal is let out of the gate, drive your animal slowly across the ring so that the judge gets a good front, rear and side view of your animal. Once all animals and exhibitors are in the ring, now is the proper time to slowly walk your animal toward the judge for a proper view. This is the first impression you will give the judge and often is the determining factor in placings. Make sure to keep eye contact with the judge and know where they're at in the ring. Also prepare for the judge to ask questions revolving around swine. - During the Show
It is important to remember that the judge is looking at how you exhibit your animal during showmanship. Many times, neat dress is a factor that comes into play. Proper dress for show day is jeans without holes or tears, leather boots, belt, and a button up shirt. It is important for you to take a brush and a rag into showmanship with you just in case your animal was to get dirty in the ring.
Exercising routinely helps your animal's growth and development as well as gives you showmanship experience


There are 8 major swine breeds that are commonly raised in the United States. On this poster I will include 5 of the major swine breeds. Different breeds are better used for specific reasons. Producers typically raise breeds that best fit their needs based on its qualities and physical characteristics. The breeds I will be educating you on are Yorkshire, Hampshire, Bluebutt, Duroc, and Berkshire.
- Yorkshire The most-recorded breed of swine in North America, Yorkshires are white with erect ears. They are found in almost every state, with the highest populations being in Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Nebraska and Ohio. Yorkshires are known for their muscle, with a high proportion of lean meat and low backfat. Soundness and durability are additional strengths.
- Hampshire The hogs with the belt. Hampshires are the fourth-most recorded breed in the United States. Most popular in the Corn Belt. Hampshires are known for producing lean muscle, high carcass quality, minimal backfat, and large loin eyes. Females also are known for their mothering ability, with longevity in the sow herd.
- Bluebutt Pigs referred to as "Blue Butts" are usually a cross between a Hampshire and Yorkshire or a Hampshire and Chester White. The resulting coat color is white hair with a "blusish" color on the rump, thus, the "Blue Butt" pig. And, yes, this pig would make an excellent 4-H animal.
- Duroc The second-most recorded breed of swine in the United States. The red pigs with the drooping ears are valued for their product quality, carcass yield, fast growth, and lean-gain efficiency. They also add value through their prolificacy and longevity in the female line. Much of the U.S. breed improvement has occurred in Ohio, Kentucky, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, and Nebraska.
- Berkshire The third-most recorded breed of swine in the United States. Berkshires are known for last and efficient growth, reproductive efficiency, cleanness, meat flavor, and value. The first US meeting of Berkshire breeders and importers was held in 1875, with the American Berkshire Association formed shortly after - making it the oldest swine registry in the world.


A Hernia is bulging of an organ or tissue through an abnormal Area. A hernia involves the stomach or intestine.
- A hernia is caused when abdominal connective tissue fails to close around the umbilical ring.
- Hernias can be hereditary, although the majority of umbilical hernias are related to infection of the umbilical cord.
- Symptoms of A hernia include
- A Bulge
- Swelling
- Pain
- Hernias are mainly located in the belly or groin areas.
- Hernia effect every species of animals but may all be caused by by different outcomes. This also affects us humans as well but a hernia can be treated.
Hernias can be prevented by improving farrowing-crate sanitation by removing accumulated sow manure before farrowing and using a powder to help keep the floor dry by doing this it may reduce bacteria and reducing the risk of a hernia.
An Affective treatment you can do for hernias are the use of Elastrator rings. These rings are a small one-inch ring that stretches to go around the hernia you would also need the use of the castration pillars to help you. Its simple and inexpensive.


- Swine influenza virus is a burden to anyone who has a swine or breeds swine because of decreased food consumption, weight loss, and possible death.
- Swine influenza is also zoonotic, meaning human's and other animals can have it as well.
- Swine influenza is caused by close contact and possibly from contaminated objects moving through infected and uninfected pigs.
- There is no affective treatment although there is medicines that can help like cough medicine, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory drug.
- Some other symptoms are fever, depression, coughing, and discharge from nose and eyes. To prevent swine influenza as much as possible look for the signs in a litter and if the symptoms are present isolate the pig from the rest of the litter.
- Swine influenza was originally found in Veracruz Mexico.


This is a disease caused by the swine pox virus which can survive outside the pig for long periods of time and is resistant to environmental changes. It is a vesicular disease, acute, often mild, infections disease characterized by skin eruptions that affects only pigs.
Causes / Contributing Factors
- It can spread by lice or mange mites
- Skin abrasions (abrasion is a wound caused by superficial damage to the skin, no deeper than the epidermis (the outer layer of cells]
- Fighting and mixing of pigs
Treatment
- No Treatment
- Condition usually resolves itself spontaneously over a three week period
Important Facts
- It will grow on pig cell cultures but not embryonating eggs
- It is relatively heat stable and survives for approx. 10 days at 37C (98 .6F)
- The disease is most frequently seen in young pigs, 3-6wk old, but all ages may be affected
- Virus is abundant in the lesions and can be transferred from pig to pig by the biting louse
- Recovered pigs are immune
- Eradication of lice is important
Symptoms
- Small circular red areas 10.20mm in diameter that commence with a vesicle containing straw-colored fluid in the center.
- After two to three days, the vesicle ruptures and a scab is formed which gradually turns black.
- The lesions may be seen on any part of the body but are common along the flanks abdomens, and occasionally the ears.


What is African Swine Fever?
African Swine Fever (ASF) is a highly contagious disease that affects swine.
It is deadly to all swine and cannot be transmitted to humans.
Symptoms of ASF
- Coughing/ difficulty of breathing
- High Fever
- Diarrhea/ vomiting
- Weakness and decreased appetite
- Red, blotchy skin lesions
ASFMore Information
ASF is not found in the US. There is no treatment or vaccine for ASF. To stop the spread, any affected swine has to be depopulated.


Minimizing heat stress in pigs during the summer
Why: Pigs can overheat very easily because they cannot sweat. Here are some ways to keep pigs cool and comfortable in summer.
- Access to Fresh Water:
Make sure pigs have access to water at all times. Pigs can easily become dehydrated in summer. Automatic watering systems work best. - Spots to Wallow:
Pigs need wallows, or mud holes to cool off. Mud is beneficial because it's cooler than air. Also when it dries on the pig it creates a protective barrier on the pigs skin to protect from the sun. - Appropriate Housing:
Pigs need housing that have plenty of ventilation and enough room to move around comfortably. Using fans can help with ventilation and help with evaporative cooling. - Wet Skin Cooling:
Pigs use evaporative cooling to lower their body heat. Spraying them down with water or setting up water drip lines or sprinklers will allow the water to dry from the pigs skin and help them cool down. - Provide Shade
Make sure to provide shade spots for your pig. Your pen should have shaded areas to protect the pig from the sun. Protecting your pig from the sun is very important. The sun can cause a pig to overheat and/or get sunburned. - Adjust Feeding Times
When temperatures rise, pigs eat less. Feeding during cooler times, like early morning and evening can help keep your pig eating and gaining weight. Providing your pig frozen treats can also help.






There is no treatment or vaccines for African swine fever because it is proven to be difficult to control transmission throughout the disease.
African swine fever can spread through ticks, feed by humans, and other pork products.
Things to be Alert About
- High fever
- Decreased appetite and weakness.
- Red, blotchy skin, or skin lesions
- Diarrhea and vomiting
- Coughing and difficulty breathing
- Abortions or sudden death
There is no other way to prevent it other then separate them from the affected and unaffected


Ear Notching, Clipping Teeth, Tail Docking, Castrating
Pig Castration
Why/When do we do it? & How do we do it?
- Castration only happens within males pigs (boars), this occurrence or castration typically happens within 7 days after birth.
- The reason for this occurrence is to reduce aggression levels, prevent unplanned pregnancies, to prevent unwanted reproduction.
- The two current ways to castrate a pig is surgical castration and immunoadsorption meaning immunoadsorption involves injection of a protein compound.
Why do we clip pigs teeth when they're born?
- Pigs usually get their teeth clipped within 7 days prior to birth.
- This task occurs to reduce injuries caused to each other and to their mother as piglets nurse.
- Some ways people clip pigs teeth is by grinding the tip, clipping the tip, or clipping the tooth at the gum line.
Left Ear Notch
- The left side ear notches helps identify a pig's litter and which one of the litter it is, giving each pig a unique identity number
- The notches are placed in 1 of 5 places on the pigs ear
Right Ear Notch
- The pigs right side of the ear helps identify the pigs litter number
- Pigs within the same litter will all have the same litter number, but will have different pig numbers
Tail Docking
We dock pig's tails to reduce tail biting in groups of pigs
- Pig's tails are supposed to be docked within the first 24 hours of birth.
- To tail dock a pig you use either side-cutter pliers (clippers) or a cauterizing tail docking iron (cauterization) and that the tail should be docked between 1.5 and 2.5 cm from the base of the tail.

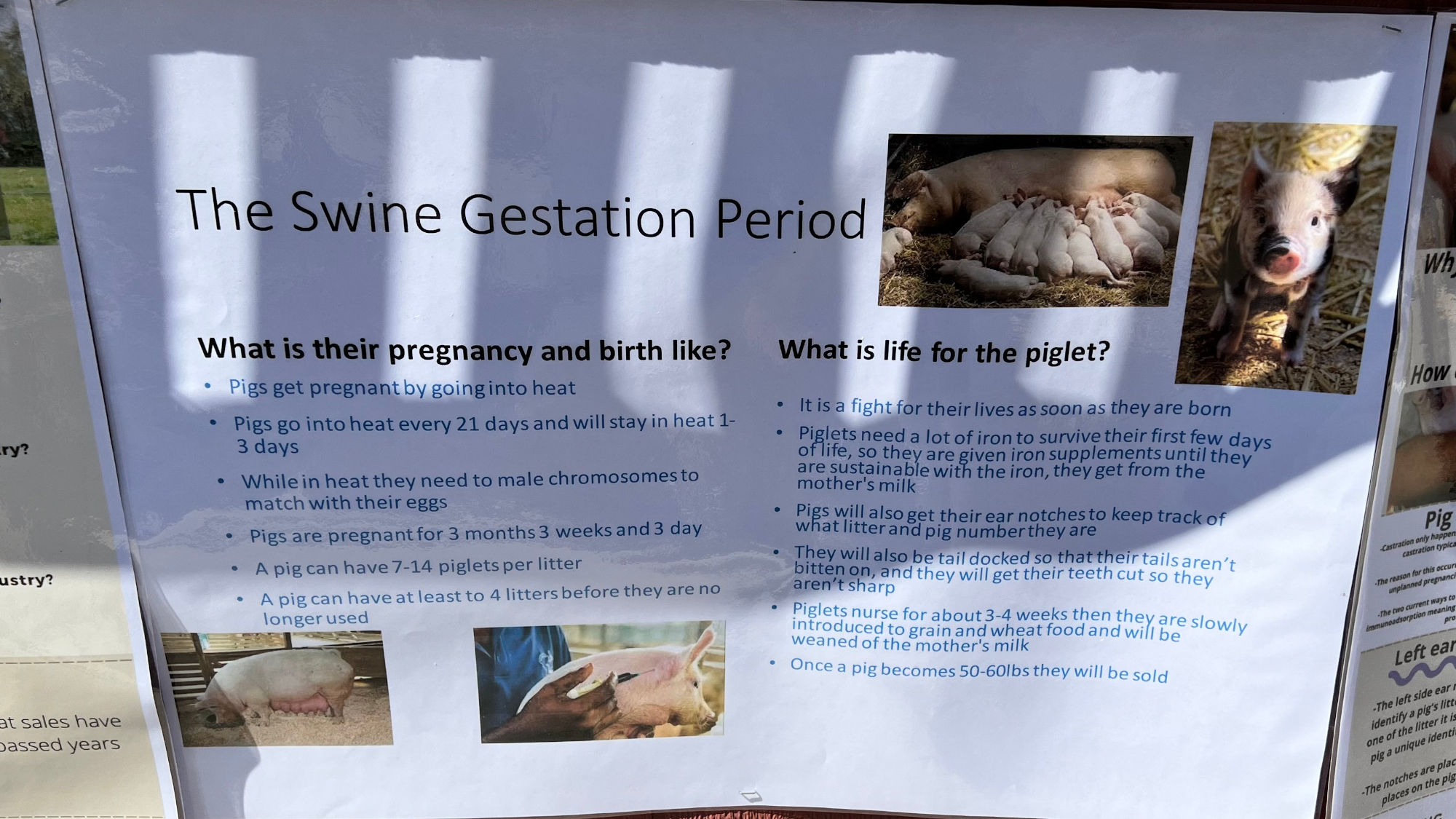
What is their pregnancy and birth like?
- Pigs get pregnant by going into heat
- Pigs go into heat every 21 days and will stay in heat 1 - 3 days
- While in heat they need male chromosomes to match with their eggs
- Pigs are pregnant for 3 months 3 weeks and 3 day
- A pig can have 7-14 piglets per litter
- A pig can have at least to 4 litters before they are no longer used
What is life for the Piglet?
- It is a fight for their lives as soon as they are born
- Piglets need a lot of iron to survive their first few days of life, so they are given iron supplements until they are sustainable with the iron they get from the mother's milk
- Pigs will also get their ear notches to keep track of what litter and pig number they are
- They will also be tail docked so that their tails aren't bitten on, and they will get their teeth cut so they aren't sharp
- Piglets nurse for about 3-4 weeks then they are slowly introduced to grain and wheat food and will be weaned off the mother's milk
- Once a pig becomes 50-60lbs they will be sold


What is Swine Pox?
Swine Pox is a viral contagious disease of pigs that are characterized by round lesions on the skin that typically heal in 3-4 weeks.
The lesions typically start with red and swollen skin and is followed by the formation of a pustule.
The colors of the lesion can go between a dark brown to a bright red.
They are able to occur all over the body of a swine and leave scars even when eventually healed.
Symptoms of Swine Pox
- Round to oval red areas less than one centimeter
- Brown/black crust around lesions
- Fluid coming out of scabs
- Lesions are easily seen on any part of the body but are most common on the flanks, abdomens, and ears
Causes of Swine Pox
- Bug bites
- Poor sanitation
- Skin abrasions
- Pig fights
- Mixing pigs together
- The spreading of lice
Treatments
- There is no real treatment
- Eventually heals on its own (3-4 weeks)
Facts about Swine Pox
- Piglets are often the carrier of the disease, but applies to all ages
- Recovered pigs are immune
- Pigs from different farms can possibly be affected from insects being carriers
- Can be transferred from pig to pig by the biting louse


Female Pigs are called gilts or sows
- Gilt is a female pig that has never had piglets
- Sow is a female pig that has had piglets
Male Pigs are called boars or barrows
- Boars are male pigs used for breeding
- Barrows are neutered male pigs that cannot breed


Right Ear Litter #
Ear notching on the right ear helps identify a pig's litter and which litter it is from. There are 5 notches on the right ear to show their litter number.
For ex. if the pig's earnotch is in the quadrant of 3 its litter number is 3.
Left Ear Pig #
Ear notching on the left ear helps identify the pig's number of their litter.
Pigs within the same litter will have the same exact litter number but different pig numbers.
There are 3 notches on the left ear. For ex. if the pig has a 1 it's pig number is 1.


- Shoulder
The pork shoulder also called the picnic shoulder is frequently cured or smoked. Pork shoulder is also used for making ground pork or sausage meat. - Loin
Hogs are bred to have extra long loins unlike lamb and beef. The entire pork loin can be roasted or it can be cut into individual chops or cutlets. The tenderloin is taken from the rear of the pork loin and baby back ribs come from the upper ribcage area ol the loin. - Belly
The pork side, also called the pork belly is also where pancetta and bacon come from. Also a part of the side of the belly is spare ribs. - Ham
The back leg of the hog is where we get fresh smoked or cured hams. Fresh hams are usually roasted but can be cut into ham steaks as well. - Jowl
The Jowl is mostly used in making sausages. Although it can also be cured and made into bacon. The jowl is located towards the front of the pig. - Boston Butt
The Boston Butt is located on the upper shoulder of the hog. Pork butt can be roasted or cut into steaks but it is also well suited for making ground pork or sausages.


- Hampshire
The hogs with "the belt," Hampshires are the fourth-most recorded breed in the United States. Most popular in the Corn Belt, Hampshires are known for producing lean muscle, high carcass quality, minimal back fat and large loin eyes. Females also are known for their mothering ability, with longevity in the sow herd. - Yorkshire
The most-recorded breed of swine in North America, Yorkshires are white with erect ears. They are found in almost every state, with the highest populations being in Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Nebraska and Ohio. Yorkshires are known for their muscle, with a high proportion of lean meat and low backfat. Soundness and durability are additional strengths. - Duroc
The second-most recorded breed of swine in the United States, the red pigs with the drooping ears are valued for their product quality, carcass yield, fast growth and lean-gain efficiency. They also add value through their prolificacy and longevity in the female line. Much of the U.S. breed improvement has occurred in Ohio, Kentucky, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, and Nebraska. - Birkshire
The third-most recorded breed of swine in the United States, Berkshires are known for fast and efficient growth, reproductive efficiency, cleanness, meat flavor and value. The first U.S. meeting of Berkshire breeders and importers was held in 1875, with the American Berkshire Association formed shortly after - making it the oldest swine registry in the world. - Spotted
The Spotted swine breed is characterized by large, black-and-white spots. Many breeders in central Indiana specialized in breeding Spotted hogs through the years. Today, Spots are known for their feed efficiency, rate of gain, and carcass quality. In addition, commercial producers appreciate Spotted females for their productivity, docility, and durability. - Chester White
Chester Whites originated in Chester County, Pa., from which their name was formed. These white hogs with droopy, medium-sized ears are known for their mothering ability, durability, and soundness. Packers also tout their muscle quality.


Importance in Ingredients
It is important that your swine feed has all the ingredients and nutrients a show hog needs.
Good pig feed contains sufficient energy, protein, minerals, and vitamins. Rice bran, broken rice, maize, soya-beans, cassava, vegetables, and distillers residues are often used in pig feed
Different Protein amounts depending on age
Depending on the age of your pig whether it was just born or ready for the fair there are different feed you feed it. Usually a young pig of 8 weeks should be given feed with 17-18% protein; older pigs must get around 15%.
Types of feed for age
Growing pigs usually from 125 - 230 should transition to a grower feed. These feeds are nutrient dense with more protein. Pigs under 40 pounds are introduced to a solid diet through creep feeding while they are still suckling.


- Notching
Ear Notching: Ear-notching helps identify a pig's litter and which one of the litter it is, giving each pig a unique identity number. - Clipping
Clipping Teeth: The purpose of teeth-clipping is to reduce injuries caused to each other and to their mother as piglets nurse. - Docking
Tail Docking: Tail docking is a common industry practice in pork production to reduce tail biting in groups of pigs. - Castrating
Castrating: Castration is performed to avoid boar taint in the meat of sexually mature male pigs and to reduce aggression toward other pigs and caretakers.








